Read this article to learn about Production Function. After reading this article you will learn about: 1. Meaning of Production Function 2. Production Function Curve 3. Types.
Meaning of Production Function:
(a) It is also known as Input Output relation.
(b) Cobb – Douglas Production function –
Q = K. LσCβ
ADVERTISEMENTS:
=K L3/4 C¼
(L = share of Labour, C= share of Capital)
Cobb – Douglas Production function is based on Constant elasticity of substitution.
Production Function Curve:
Explanation of Production Function Curve:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
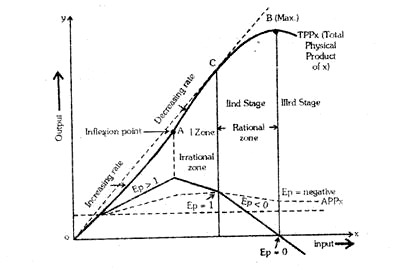
(a) Total Physical Product of x (TPPx) rises at increasing rate of return; MPPx rising and production function curve is concave upward.
(b) Beyond Inflexion point ‘A’, TPPx rises but at diminishing rate & MPPx starts to decline.
(c) TPPx is highest at point ‘B’ or remains constant; and MPPx = 0.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(d) TPPx decreases then MPPx become negative.
(e) At point ‘D’; MPPx = APPx and APPx is maximum.
(f) When MPPx > APPx; then APPx is increasing.
(g) When MPPx < APPx; then APPx; is decreasing but never becomes negative.
(i) When α+β = 1 →Law of constant return
(0 When α+β >1 →Law of increasing return
(J) When α+β ˃1→ Law of diminishing return
Types of Production Function:
(a) Linear P.F. When P.F. is homogeneous of the first degree
Y = a0+a1xa1+a2x2+ ____________anxn
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(Where Y = Production, a0 = Constant, a1 a2 …..an = Coefficient factors, X1,X2..Xn= Factors of Production)
(b) Quadrate P.F→Y= a+bx+cx2
(Where a, b, c = constant, x = Production factor)
(c) Square root P.F. Y= a+b√x1+cX2
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(d) Cubic P.F. Y = a0+a1x+b2x2+a3x3
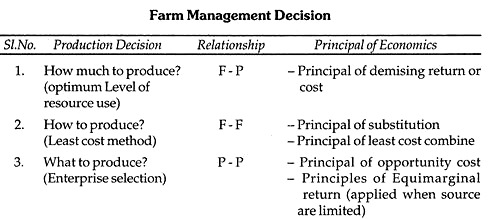
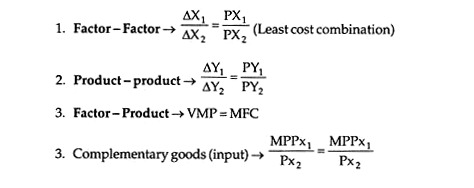
(i) Maximum profit is obtained when. Marginal Return = Marginal Cost
(ii) Breakeven point → Total Return = Total Cost
(iii) Acc. To law of diminishing return, optimum profit will be at a point where, MC = MP
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(iv) Optimum level of input use without resource limitation Law of diminishing return (F-P)
(v) Division under resource limitation Principal of equimarginal return (P- P)
(vi) Chose best crop enterprises Principal of opportunity cost (P-P)
(vii) Dept.-equity ratio = Differed liabilities /Net worth
(viii) A- Net capital ratio = Total Assets/Total liabilities.
(ix) When MPP is maximum, the MC will be lowest.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(x) MPP zero – When MC is minimum.
(xi) Rate of Turn Over = Gross Income / Total Assets x 100
(xii) Present value of future money is calculated by use of = P/ (1+i) t
(xiii) B. C ratio = Benefit/total cost (Mostly used to evaluate construction of Dam)
Relationship:
Elasticity of Production:
(a) When MP = 0, then Ep = 0 → Completely inelastic demand
(b) When MP = AP, then EP = 1→ Unit inelastic demand (Ex. Demand of Agri. Products)
(c) When MP > AP, then EP > 1 → Elastic demand (for monopoly)
(d) When MP = AP, then Ep < 1→ Relatively inelastic demand,
(e) When demand curve is flatter – Relatively elastic demand
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(f) Perfect elasticity = Horizontal straight line. Perfect inelastic = Vertical demand curve for a commodity.
(g) Relatively elastic = Flatter demand curve.