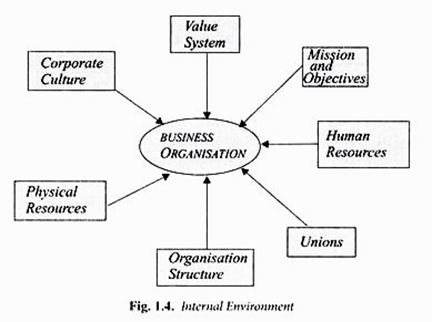
The following points highlight the seven factors that determine internal environment of a business firm.
The factors are: (1) Value System, (2) Mission and Objectives, (3) Organisation Structure, (4) Corporate Culture and Style of Functioning of Top Management, (5) Quality of Human Resources, (6) Labour Unions, and (7) Physical Resources and Technological Capabilities.
Internal Environment of a Business
Factor 1# Value System:
The value system of an organisation means the ethical beliefs that guide the organisation in achieving its mission and objective. The value system of a business organisation also determines its behaviour towards its employees, customers and society at large. The value system of the promoters of a business firm has an important bearing on the choice of business and the adoption of business policies and practices. Due to its value system a business firm may refuse to produce or distribute liquor for it may think morally wrong to promote the consumption of liquor.
The value system of a business organisation makes an important contribution to its success and its prestige in the world of business. For instance, the value system of J.R.D. Tata, the founder of Tata group of industries, was its self-imposed moral obligation to adopt morally just and fair business policies and practices which promote the interests of consumers, employees, shareholders and society at large. This value system of J.R.D. Tata was voluntarily incorporated in the articles of association of TISCO, a premier Tata company.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Infosys Technologies which won the first national corporate governance award in 1999 attributes its success to its high value system which guides its corporate culture. To quote one of its reports, “our corporate culture is to achieve our objectives in environment of fairness, honesty, transparency and courtesy towards our customers, employees, vendors and society at large” Thus value system of a business firm has an important bearing on its corporate culture and determines its behaviour towards its employees, shareholders and society as a whole.
Factor 2# Mission and Objectives:
The objective of all firms is assumed to be maximization of long-run profits. But mission is different from this narrow objective of profit maximization. Mission is defined as the overall purpose or reason for its existence which guides and influences its business decision and economic activities.
The-choice of a business domain, direction of its development, choice of a business strategy and policies are all guided by the overall mission of the company. For example, “to become a world-class company and to achieve global dominance has been the mission of ‘Reliance Industries of India’. Similarly “to become a research based international pharma company” has been stated as mission of Ranbaxy Laboratories of India.
Factor 3# Organisation Structure:
Organisation structure means such things as composition of board of directors, the number of independent directors, the extent of professional management and share -holding pattern. The nature of organisational structure has a significant influence over decision making process in an organisation. An efficient working of a business organisation requires that its organisation structure should be conducive to quick decision making. Delays in decision making can cost a good deal to a business firm.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The board of directors is the highest decision making body in a business organisation. It takes general policy decisions regarding direction of growth of business of the firm and supervises its overall functioning. Therefore, the managerial capability of the board of directors is of crucial importance for the functioning of a business firm and for achievement of its overall mission and objectives.
For efficient and transparent working of the board of directors in India it has been suggested that the number of independent directors be increased. Many private corporate firms in India are managed by family members of their promoters which is not conducive to the efficient working of these firms.
It is therefore highly desirable to increase the extent of professional management of private corporate companies. The share holding pattern has also an important implication for business management. In some Indian companies the majority of shares is held by the promoters of the company themselves.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
In some others share-holding pattern is quite diversified among the public. In India financial institutions such as UTI, LIC, GIC, IDBI, IFC etc. have large share holdings in prominent Indian corporate companies and the nominees of these financial institutions play a critical role in making major business policy decisions of these corporate companies.
Technically, shareholders elect directors who make up the board of directors. The directors then appoint company’s top managers who take various business decisions. However, most of the shareholders delegate the voting rights to the management or do not attend the general body meeting.
Thus, most of the shareholders regard ownership of the company as a purely financial investment. However, in recent years in developed countries like the United States the shareholders have come to wield a great influence.
The bankruptcy of business giants such as Enron, World Com. in the United States have created great awareness as well as mistrust among shareholders. In the last few years there has been frequent law suits filed by shareholders against directors and managers for ignoring the interests of shareholders or in fact cheating them by not declaring dividends. That is why there is worldwide debate on proper corporate governance of business firms.
Factor 4# Corporate Culture and Style of Functioning of Top Management:
Corporate culture and style of functioning of top managers is important factor for determining the internal environment of a company. Corporate culture is generally considered as either closed and threatening or open and participatory.
In a closed and threatening type of corporate culture the business decisions are taken by top-level managers, while middle level and work-level managers have no say in business decision making. There is lack of trust and confidence in subordinate officials of the company and secrecy pervades throughout in the organisation. As a result, among lower level managers and workers there is no sense of belongingness to the company.
On the contrary, in an open and participatory culture, business decisions are taken at lower levels of management, and top management has a high degree of trust and confidence in the subordinates. Free communication between the top level management and lower-level managers is the rule in this open and participatory type of corporate culture. In this open and participatory system the participation of workers in managerial tasks is encouraged.
Closely related to corporate culture is the style of functioning of top management. Some top managers believe in just giving orders and want them to be strictly followed without holding consultations with lower level managers. This style of functioning is not conducive to the adaptability and flexibility in dealing with the changing external environment of business.
Factor 5# Quality of Human Resources:
Quality of employees (i.e. human resources) of a firm is an important factor of internal environment of a firm. The success of a business organisation depends to a great extent on the skills, capabilities, attitudes and commitment of its employees. Employees differ with regard to these characteristics.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
It is difficult for the top management to deal directly with all the employees of the business firm. Therefore, for efficient management of human resources, employees are divided into different groups. The manager may pay little attention to the technical details of the job done by a group and encourage group cooperation in the interests of a company. Due to the importance of human resources for the success of a company these days there is a special course for managers how to select and manage efficiently human resources of a company.
Factor 6# Labour Unions:
Labour unions are other factor determining internal environment of a firm. Unions collectively bargain with top managers regarding wages, working conditions of different categories of employees. Smooth working of a business organisation requires that there should be good relations between management and labour union.
Each side must implement the terms of agreement reached. Sometimes, a business organisation requires restructuring and modernisation. In this regard, the terms and conditions reached with the labour union must be implemented in both letter and spirit if cooperation of workers is to be ensured for the reconstruction and modernisation of business.
Factor 7# Physical Resources and Technological Capabilities:
Physical resources such as plant and equipment, and technological capabilities of a firm determine its competitive strength which is an important factor determining its efficiency and unit cost of production. R and D capabilities of a company determine its ability to introduce innovations which enhance productivity of workers.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
It is however important to note that rapid technological progress, especially unprecedented growth of information technology in recent years has increased the relative importance of ‘intellectual capital and human resources as compared to physical resources of a company. The growth of Bill Gates Microsoft Company and Murthy’s Infosys Technologies is mostly due to the quality of human resources and intellectual capital than to any superior physical resources.