“Correlation analysis deals with the association between two or more variables.” —Simpson and Kafka
“Correlation is an analysis of the co-variation between two variables.” —A.M. Tuttle
“Correlation analysis shows us the degree to which variables are linearly related.” —Wonnacott and Wonnacott
Although Karl Pearson was the first to establish the mathematical formula but Sir Francis Galton was the first to develop the technique to obtain it graphically.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
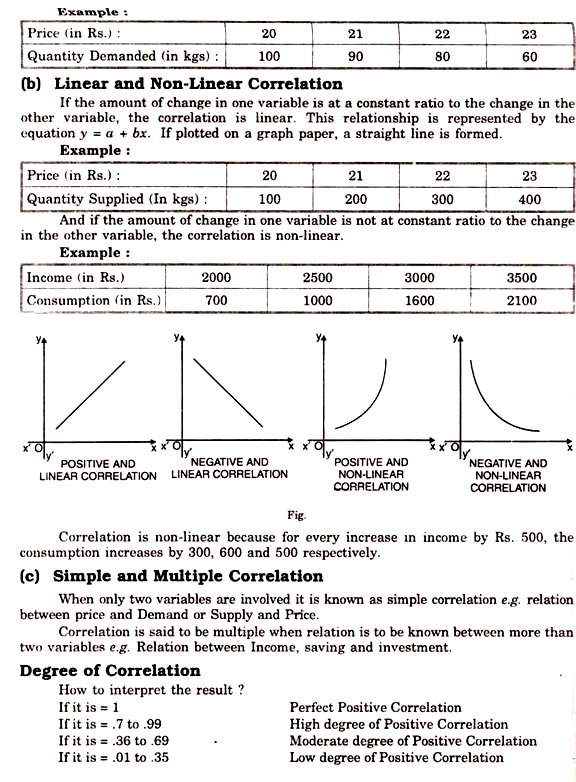
Types of Correlation:
(a) Positive and Negative Correlation:
On the basis of the direction of the change in two variables, correlation can be negative or positive. If the change in both variables is in the same direction, the correlation is positive. In other words, if X increases, Y also increases and if X falls, Y also falls
Example:
If the change in both the variables is in the opposite direction, then correlation is negative, or, if X increases Y decreases and if X decreases Y increases.
Cause and Effect Relationship:
With the increase in one variable other increases or decreases, but it is not necessary that this change is due to the change in first variable.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(1) Both the variables may be affected by some external factor. There is no correlation between the price of wheat and price of wine. But still the prices of both have increased. And it is due to an external factor i.e. inflation.
(2) We know that it price increases there is increase in supply. But increase in supply may be due to the up gradation of technology; And due to better technology price may go up due to better quality.
(3) If sample is small cause and effect relationship can’t be tried.
(4) Personal bias of the investigator can also change the magnitude of prices.
Methods to Calculate Correlation:
Correlation can be measured by the following methods:
(A) Graphical Methods:
(a) Scatter diagram or Scattergram.
(b) Simple graph or graphic Method.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(B) Mathematical Methods:
(1) Karl Pearson’s Coefficient of Correlation Method or Karl Pearson’s method.
(2) Spearman’s Coefficient of Correlation Method or Rank Difference Method.
(3) Concurrent Deviations Method.