The below mentioned article provides a beginner’s guide to demand forecasting.
This article will help you to understand the following things:- 1. Definition of Demand Forecasting 2. Factors Involved in Demand Forecasting 3. Types 4. Essentials 5. Importance 6. General Approach 7. Additional information.
Definition of Demand Forecasting:
Demand forecasting helps a firm to assess the probable demand for its products and plans its production accordingly.
Demand forecasting is very important in industrially developed countries where supply position is at ease and the demand position is always uncertain.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
But in developing countries, like India supply factor is the limiting factor. So here supply forecasting is more important than the demand forecasting. After the two recessions in India i.e., of 1967-68 and 1974-76. Demand forecasting is bound to become more important.
1. In simple words — “Demand forecasting is an estimate of future sales”.
2. From a Company’s or Firm’s point of view — “Demand Forecasting means deciding in advance its share in the Total Market Demand”.
This estimate is made considering various factors like:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(i) Controllable and non-controllable, and
(ii) Present and anticipated market conditions.
3. In the words of Phillip Kotler — “The company demand forecast is expected level of company demand based on a chosen marketing plan and assumed environmental conditions.”
4. Cundiff and Still has said — “Demand forecasting is an estimate of sales during a specified, future period, which is tied to a proposed marketing plan and which assumes a particular set of uncontrollable and competitive forces.”
ADVERTISEMENTS:
5. According to Marketing Association — “An estimate of demand in dollars or physical units for a specified future period under a proposed marketing plan or programme and under an assumed set of economic and other forces outside the unit for which the forecast is made. The forecast may be for a specified item of merchandise or for entire line,”
Factors Involved in Demand Forecasting:
Factors that are involved in demand forecasting are as follows:
1. Period of Forecasting:
Demand forecasting may be for:
(i) Short-term, or
(ii) Long-Urn,
Short-term demand may cover a period of three months, six months or one year but not exceeding one year. Long-term or Long-run forecasting covers a period exceeding five years. A business should forecast short-term as well as long-term demand for its products to have a clear view of business activities.
An alternative method may be to associate the long-term and short-term forecasting with certain types of decisions. Thus, short-term forecast is one which provides information for day to day operations within the limits of resources currently available. Whereas long-term forecasting is more concerned with decisions extending or reducing the units of resources.
2. The Forecast may be General or Specific:
General forecast may be useful for the firm but it also needs commodity forecasts and sales area forecasts (specific forecasts).
3. Demand Forecasting may be Undertaken of Three Different Levels:
(a) Macro Level.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(b) Industry Level.
(c) Firm Level.
(a) Macro Level:
It is concerned with business conditions over the whole economy measured by an approximate index of industrial production, national income or expenditure. This kind of external data covers the basic assumptions on which the business must have a base for its forecasts.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(b) Industry Level:
This includes the preparations of demand forecasting by different trade associations.
(c) Firm Level:
It is an important matter from the management point of view. Individual firms mostly forecast their sales.
4. Methods and Problems of Demand Forecasting be Studied thoroughly and Separately:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Problems of demand forecasting are quite different from products, therefore this may be studied separately and vigorously.
5. Various Factors Affecting the Demand of Consumer and Capital Goods are Studied:
The distinctive patterns of demand for different category of this economic analysis of consumer and capital goods be studied thoroughly, so that the position of demand may be known.
6. In Every Demand Forecast Every Product has Special Factors of its Own:
If there is competition in the market, situation may be different and complicated with uncertainty or un-measureable risk, error or inaccuracy in the forecast.
7. Sociological Factors need not be Left Unattended:
This factor has been considered as important from practical and social point of view.
Types of Forecasting According to Time:
Forecasting according to time may be of two types:
1. Short-term and
ADVERTISEMENTS:
2. Long-term
(A) Short-Term Forecasting:
Short-term forecasting is of following types:
1. For evolving suitable production policy:
This policy is evolved to avoid the problem of over-production and under-production.
2. In Reducing cost of purchasing raw-materials:
This is used in helping the firm in reducing the cost of purchasing raw-materials and controlling inventory by assuring regular supply of raw-materials.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
3. It is helpful in determining appropriate price policy:
So as to avoid an increase when the market conditions are expected to be weak and a reduction when a market is going to be quite strong.
4. Helpful in setting sales targets and establishing controls and incentives:
If targets are set too high, they will be discouraging salesman who fails to achieve them, if set too low, the targets will be achieved easily and hence incentives will prove meaningless. A comparison between ‘Targeted Sales’ and ‘Actual Sales’ will help the management to control selling and salesmen activities.
5. Helpful in forecasting short-term financial requirements:
Cash requirements depend on sales level and production operations. Sales forecasts enable arrangement of sufficient funds on reasonable term well in advance.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
6. Helpful in arranging the labour force:
Demand forecasting helps management in arranging the labour force trained and untrained for maintaining a continuous flow of production and to avoid any obstruction in the process of production due to shortage of labour and to avoid the problem of surplus labour.
(B) Long-Term Demand Forecasting:
Long-term demand-forecasting helps in the following manner:
1. It helps to plan for new units or at the same existing units to expand their activities:
A long-term demand forecasting helps the existing hints to expand their activities. A multiproduct firm must determine total demand situation and the demand for different items.
2. It is helpful in planning for long-term financial requirements:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
If the demand is more and it takes long-time then such long-term financial requirements could be planned and funds may be arranged and made available at the right time.
3. It is helpful in drawing man power planning:
The availability of trained and experienced man-power in requisite number should be planned in advance on the basis of long-term sales forecasting. Training and personal development and long-term preposition and need considerable time to complete. The development of these two potentials should be planned well in advance.
Essentials of a Good Forecasting Method:
A good system of forecasting must have the following qualities:
1. Simplicity and Ease of Comprehension:
Complicated, mathematical and statistical techniques may be avoided. System adopted should be that management must be able to understand and have confidence in the techniques used.
2. Economy:
Cost must be weighed against the importance of the forecast to the operations of the business. The criticism should be the economic consideration of balancing the benefits from increased accuracy against the extra cost of providing the improved forecasting.
3. Availability of Useful Information:
Techniques should give quick results and useful information.
4. Durability of the Forecasting:
Durability of the forecasting, power of a demand and functions depends on reasonableness and simplicity of functions filled.
5. Accuracy:
Demand forecasting is the basis of marketing, planning and therefore, sales forecasts should be as much accurate as possible.
Importance of Demand Forecasting:
Demand forecasting has the following importance:
1. Essential to Produce the Required Quantities at the Right Time:
Accurate demand forecasting is essential for a firm to enable it to produce the required quantities at the right time and arrange well in advance for the various factors of production. The producer can frame a suitable production policy. The firm can reduce costs of purchasing raw-materials.
2. To Adopt Suitable Price Policy:
It also enables the firm to adopt a suitable price policy. It is on the basis of demand and sales forecasts that arrangements are made for raw-materials, equipment, machine, accessories, labour and buildings well in advance and at the right time.
3. It is Very Popular in Industrially Advanced Countries:
Demand forecasting is very popular in industrially advanced countries. This is bound to become more popular and important with the growing industrialisation of the country.
4. It is Helpful in the Maximisation of Profit:
A firm can maximise its profits only when it produces on the basis of the demand of its products. There will be no problem of over and under production if the figure of demand forecasts is accurate. As it will reduce or have control over costs, the profits will certainly go up. The importance of sales forecasting is much more in large scale or seasonal industries.
5. Importance from National Point of View:
On the national level, demand forecasts of particular products may provide guideline for demand forecasts for related industries.
For example:
A demand forecasts for cotton textile may provide an idea of probable demand for textile machinery, readymade garments, dye stuff industries. The government on the basis of sales forecasts may decide whether imports are necessary to meet the deficit in the home demand or may provide export incentives for any surplus. Thus, demand forecasts are useful to the firm, industry and also to the government.
General Approach to Demand Forecasting:
The following steps are necessary:
1. Clearly state the objectives of forecasting—Identify and clearly state the objectives of forecasting. Short-term or long-term market share or industry as a whole.
2. Select the appropriate method of forecasting.
3. Identify the variables affecting the demand for product and express them in appropriate form.
4. Collect and gather relevant data and approximations to relevant data to represent the variables.
5. Determine the most probable relationship-through the use of the statistical techniques determine the most probable relationship between the dependent and the independent variables.
6. Prepare the forecast and interpret the results. Interpretation is more important to the management.
7. For forecasting the Company’s share in the demand two different assumptions can be made:
(a) The ratio of the company sales to the total industry sales will continue as in the past.
(b) On the basis of an analysis of likely competition and industry trends, the company may assume a market share from that of the past. As forecasts are based on certain assumptions, they must be revised when improved information is available. In long-term forecasts, the projection may be revised yearly. These are sometimes also known as Rolling Forecasts.
8. Forecasts may be made either in terms of physical units or interns of rupees of sales volumes.
9. Forecasts may be made in terms of product groups and then broken for individual products on the basis of past percentages. These products groups may be divided into individual products in terms of sizes, brands, labels, colours etc.
10. Forecasts may be made on annual basis and then divided month-wise or week-wise on the basis of past records.
11. For determining the month-wise break-up of the forecast sales of a New Product, either use may be made of other firm’s data if available or some survey may be necessary.
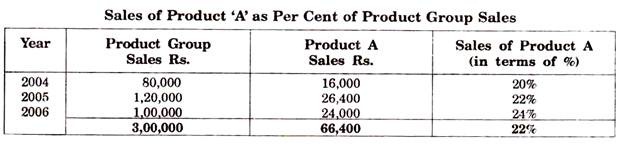
Illustration:
The following illustration shows how a sales forecast in terms of product group can be divided into individual products:
Suppose, that the forecast of product group sales for 2007 are Rs. 1,50,000. For calculating the forecast sales of product A, we can take either percentage revealed by the trend (which in this case would be 26 assuming that the same growth trend continuous) or the average percentage which would be 22. Sales forecast for product A on the basis of average percentage is Rs. 33,000 and on the basis of 26% is Rs. 39,000.
Additional Information:
Demand Forecasting of a New Product:
JOEL DEAN has suggested a number of possible approaches to the problem of forecasting demand for a NEW PRODUCTS.
(1) Project the demand for new goods as an outgrowth of an existing Old Products.
(2) Analyse the new goods as substitute for some existing goods or service.
(3) Estimate the rate of growth and the ultimate level of demand for goods on the ground of the pattern of growth of established goods.
(4) Estimate the demand by making direct enquiries from the ultimate purchases either by the utility of samples or on a full scale.
(5) Offer the new goods for sale in a sample market i.e., by direct mail or throughout Multiple Shop Organisation.
(6) Survey consumer’s reactions to new goods indirectly through the eyes of specialised dealers who are thought to be in touch with the consumers of the product and are well informed about their necessities and choice.