In this article we will discuss about the nature of the types of change in demand for goods, explained with the help of a diagram.
The demand for a good may change owing to a change in its price and it may also change because of a change in some other demand determinant, e.g., income. However, the nature of these two types of change in demand is not the same. The former results in a movement along a particular demand curve.
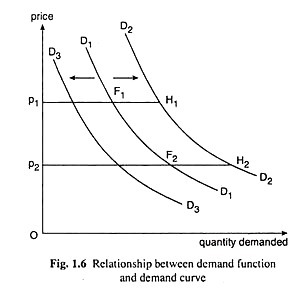
For example, if the demand curve for the good is D1D1 in Fig. 1.6, a change (fall) in price from p1 to p2 results in an increase in demand for the good from p1F1 to p2F2, move downward towards right from the point F1 to F2 along the demand curve. Similarly, if there is a rise in price, rise upward towards left along the same demand curve.
On the other hand, the second type of change in demand which happens because of a change in some demand determinant(s) other than (own) price of the good, results in a shift in the demand curve. For example, in Fig. 1.6, suppose that, initially, the demand curve for the good is D1D1. If now income of the buyers increases, the market demand for the good would also increase at each price.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Suppose, at the price of p1, demand increases from p1F1 to p1H1 and at the price of p2, it increases from p2F2 to p2H2. Therefore, after the increase in income the (market) demand curve for the good would shift rightward from D1D1 to D2D2, the latter curve passing through the points H1, H2, etc.
Similarly, if the income of the buyers decreases, the demand curve would shift to the left from the initial curve, D1D1, to a curve like D3D3.
In order to make a difference between the two types of change in demand, two different names for these changes are used. Change in demand owing to a change in (own) price of the good is called change (increase or decrease) in quantity demanded.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
As a result of this change, a movement takes place along the (same) demand curve. On the other hand, change in demand owing to a change in some demand determinant other than the (own) price, is called change (increase or decrease) in demand-it may also be called expansion or contraction in demand. As a result of this change, the demand curve for the good itself shifts to the right or to the left.