It is the simplest of the values of Dispersion. It is merely the difference between the largest and smallest term. Symbolically;
or Range = Largest term-Smallest term.
And Coefficient of Range = L-S/L+S
ADVERTISEMENTS:
It is also known as Ratio of Range or Co-efficient of Scatteredness.
If the averages of the two distributions are close to each other, a comparison of the ranges shows that the distribution with the smaller range has less dispersion. The average of that distribution is more typical of the group.
How to Compute Range Individual Series:
Example 1. Find Range and Coefficient of Range for following data.
Solution:
Here L =45 and S=3;
Range=L-S =45-3= 42
And Co-efficient of Range = L-S/L-S =45-3/45+3 = 42/48= .875
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(Note. Here Range is Absolute measure and Co-efficient of Range is Relative measure)
Discrete Series:
Example 2. Find Range and Coefficient of Range for following data:
Solution:
Going through the variables S = 5 ; and L = 40 .•. Range = 40-5 = 35… [R=L-S]
[C.R.=L-S/L+S]
And Coefficient of Range=40-5/40+5= .778
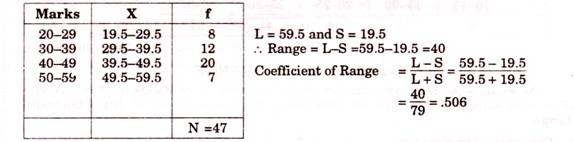
Continuous Series
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Example 3. Find ‘Range and ‘Coefficient of range’ of the following data:
Solution:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(Note. You may take the Mid Points of Class intervals and get the result. So any of the methods can be applied)