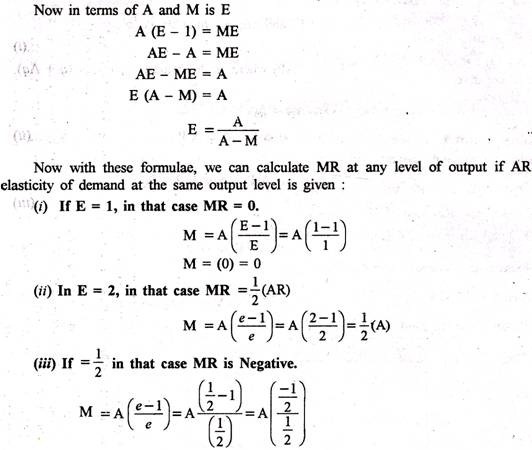Relationship between AR, MR and Elasticity of Demand!
The relationship between AR, MR and elasticity of demand is very useful at any level of output.
This relationship is very useful in the price-determination under different market conditions. It has been discussed that average revenue curve of a firm is the same thing as the demand curve of the consumer for the product of the firm.
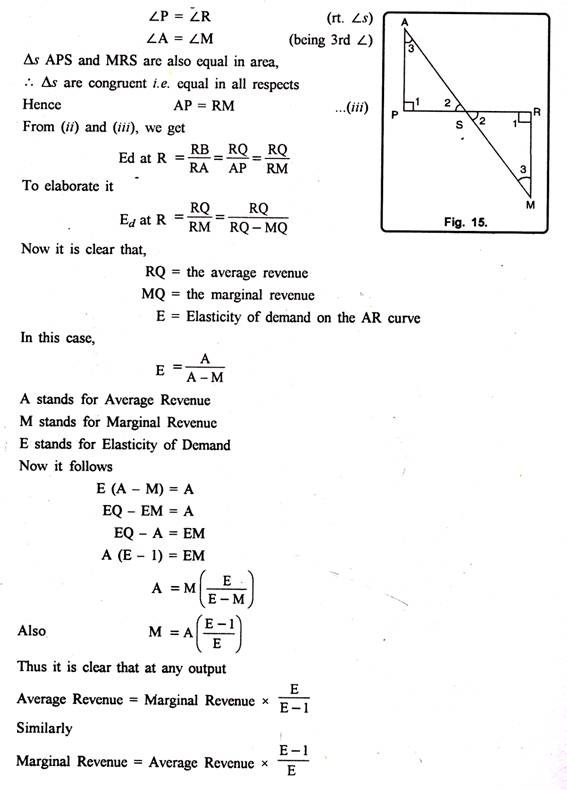
It means AR curve is from the point of view of seller but the same is the demand curve from the consumer’s point of view. It means elasticity of demand at any point on the demand curve is the same thing as the elasticity on the demand curve. Before we discuss the mutual relationship between AR, MR and Elasticity of demand, let us study these concepts briefly. AR is the revenue per unit of output sold. AR is the ratio of TR to total output. Besides, AR is nothing but the price.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
It can be seen as:
Alternative Algebraic Formula:
Thus, it is clear that at different levels of output where elasticity of demand is greater than one, the marginal revenue will be positive. On the other hand, if the elasticity of demand is equal to one, in that case the MR = 0. Lastly, if elasticity of demand is less than one, in that case MR will be negative.
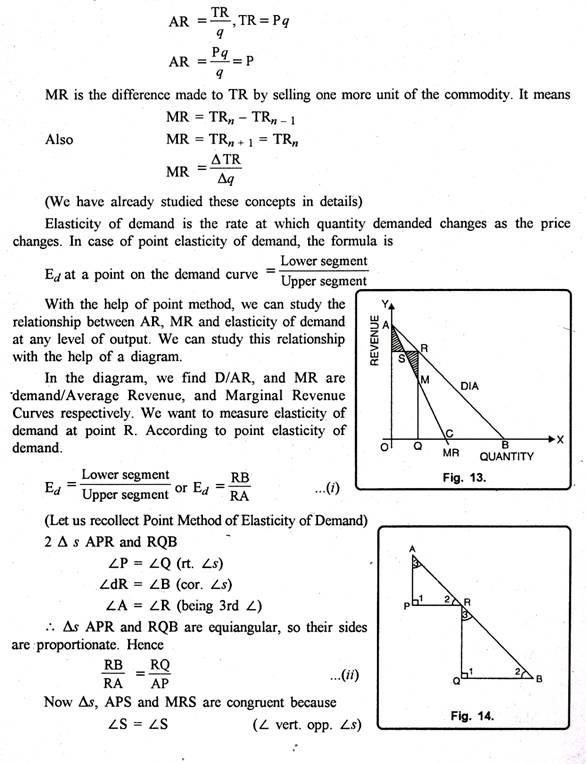
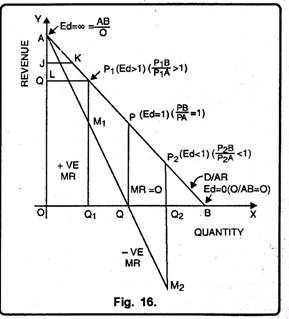
This can be made further clear with the help of a diagram given below:
If elasticity of demand is equal to one or E = 1, in that case MR = 0. OQ quantity is demanded at EQ price. At this E = 1 because P is in the centre of AB demand curve. In this case, you see MR curve touches the X-axis at point Q. It show; MR = 0.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
If E > 1, in that case MR will be positive. OQ1 quantity is demanded at P1Q1 price. At P1 elasticity of demand is greater than one i.e. E > 1. The MR for OQ1output is M2Q2 which is positive.
At OQ2 output AR = P2Q2 elasticity of demand at is less than one, so MR is M2Q2 which is negative.