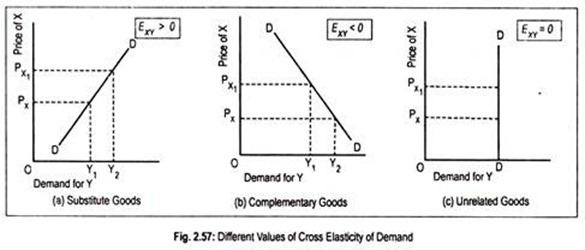
The below mentioned article provides study notes on cross elasticity of demand.
EXY = % change in quantity demanded for Y/% change in price X
EXY = ∆QY/QY/∆PX/PX = ∆QY/∆PX. PX/QY
Cross elasticity may be positive or negative, depending on the relationship between the two commodities. If the commodities are substitutes, cross elasticity will be positive, i.e., a rise in the price of the first commodity will cause an increase in the demand for the other commodity.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Fig. 2.57(a) shows the relationship between PX and demand for substitute good, Y. If X and Y are substitutes then the quantity demanded for Y is directly related to the price of X. As PX rises to PX1, demand for Y rises from OY1 to OY2.
If they are complements then quantity demanded for Y is inversely related to the price of X. In Fig. 2.57(b) demand curve has a negative slope. An increase in the price of X from PX to PX1 leads to a fall in the demand for Y. Thus cross elasticity of demand has a negative value. Thus for substitute goods, cross elasticity of demand becomes positive and for complementary goods it is negative.
If goods X and Y are not related either way (say, good X is a calculator while good Y is a trouser) then the value of cross elasticity of demand becomes zero. Fig. 2.57(c) shows zero cross-elasticity of demand A rise or fall in the price of X does not result in a change in the demand for Y.