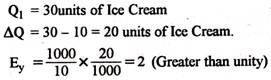Income Elasticity of Demand: Definition, Degrees and Measurement of Income Elasticity!
According to Stonier and Hague, “Income elasticity of demand shows the way in which a consumer’s purchase of any good changes as a result of change in his income”.
It shows the responsiveness of a consumer’s purchase of a particular commodity to a change in his income. Income elasticity of demand means the ratio of percentage change in the quantity demanded to the percentage change in income.
In brief income elasticity, i.e.,
Definitions:
“Income elasticity of demand means the ratio of the percentage change in the quantity demanded to the percentage change in income.” Watson
“The responsiveness of demand to change in income is termed as income elasticity of demand.” Richard G. Lipsey
Degrees of Income Elasticity of Demand:
(i) Positive Income Elasticity of Demand:
Positive income elasticity of demand is said to occur when with the increase in the income of the consumer, his demand for goods and services also increases and vice-versa. Income elasticity of demand is positive in case of normal goods.
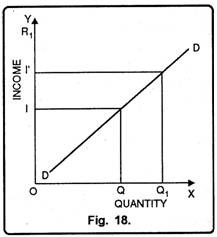
In fig. 18, quantity of commodity ‘I’ has been measured on X-axis and income of the consumer on Y- axis. DD is the positive income elasticity of demand curve. It slopes upward from left to right indicating that increase in income is accompanied by increase in demand of goods and services and vice-versa.
1. Income Elasticity is Unity:
The change in demand is proportionate to the change in income.
For example:
Income Elasticity = 1 when 25% change m income / 25% change in demand = 1
ADVERTISEMENTS:
2. Income Elasticity Greater than One:
When the change in demand is more than proportionate change in income, income elasticity of demand is greater than one or unity.
For example:
Income Elasticity > 1 when 15% change in income / 15% change in demand = 1.5
3. Income Elasticity Less than One:
If change in demand is less than proportionate change in income, income elasticity of demand is less than one or unity.
For example:
Income Elasticity < 1 if 20% Change in income / 20% change in demand = 0.5
(ii) Negative Income Elasticity of Demand:
Negative income elasticity of demand is said to occur when increase in the income of the consumers is accompanied by fall in demand of goods and services and vice-versa. It is the case of giffen goods.
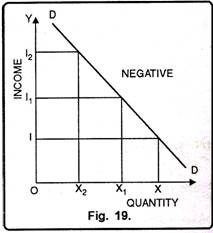
In fig. 19 when income of the consumer is 01, demand for goods and services is OX. Now as the income increases to I1, quantity demanded falls to OX1. Again as the income increases to I2, quantity demanded falls to OX2. DD is the negative income elasticity of demand curve.
(iii) Zero Income Elasticity of Demand:
Zero income elasticity of demand is said to exist when increase or decrease in income has no impact on the demand of goods and services.
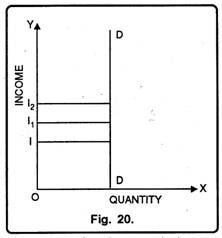
In fig. 20 initially when income is 01, quantity demanded is OD. Now, income increases to OI2 demand remains constant i.e. OD. Even when income reduces to OI1, quantity demanded remains OD. Generally, as income increases demand for goods increases. But in some cases, demand may not change to change in income or demand may diminish for an increase in income. The former case represents zero income elasticity.
Income elasticity is zero if a change in income fails to produce any change in demand. Income elasticity is negative, if an increase in income leads to a reduction of demand. This happens only in the case of inferior goods. But in all other cases it is positive. In short income elasticity is greater than one for luxuries but less than one for necessaries.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Measurement of Income Elasticity:
Income elasticity can be measured with the help of following formula: