In this essay we will discuss about National Income. After reading this essay you will learn about: 1. Definitions of National Income 2. Concepts of National Income 3. Methods 4. Importance.
Concepts:
- Essay on the Definitions of National Income
- Essay on the Concepts of National Income
- Essay on the Methods of Measuring National Income
- Essay on the Importance of National Income
Essay # 1. Definitions of National Income:
The definition of national income can be grouped into two classes. One, the traditional definitions advanced by Marshall, Pigou and Fisher, and two, modern definitions.
The Marshallian Definition:
According to Marshall:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
“The labour and capital of a country acting on its natural resources produce annually a certain net aggregate of commodities, material and immaterial including services of all kinds…This is the true net annual income or revenue of the country or national dividend.”
In this definition, the word ‘net’ refers to deductions from the gross national income in respect of depreciation and wearing out of machines. And to this, must be added income from abroad.
It’s Defects. Though the definition advanced by Marshall is simple and comprehensive, yet it suffers from a number of limitations.
First, in the present day world, so varied and numerous are the goods and services produced that it is very difficult to have a correct estimation of them. Consequently, the national income cannot be calculated correctly.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Second, there always exists the fear of the mistake of double counting, and hence the national income cannot be correctly estimated. Double counting means that a particular commodity or service like raw material or labour, etc. might get included in the national income twice or more than twice.
For example, a peasant sells wheat worth Rs 2000 to a flour mill which sells wheat flour to the wholesaler and the wholesaler sells it to the retailer who, in turn, sells it to the customers. If each time, this wheat or its flour is taken into consideration, it will work out to Rs 8000, whereas, in actuality, there is only an increase of Rs 2000 in the national income.
Third, it is again not possible to have a correct estimation of national income because many of the commodities produced are not marketed and the producer either keeps the produce for self-consumption or exchanges it for other commodities. It generally happens in an agriculture-oriented country like India. Thus the volume of national income is underestimated.
The Pigovian Definition:
Marshall’s follower, A.C. Pigou, has in his definition of national income included that income which can be measured in terms of money. In the words of Pigou, “National income is that part of objective income of the community, including of course income derived from abroad which can be measured in money.” This definition is better than the Marshallian definition. It has proved to be more practical also.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
While calculating the national income now-a-days estimates are prepared in accordance with the two criteria laid down in this definition. First, avoiding double counting, the goods and services which can be measured in money are included in national income and Second income received on account of investment in foreign countries is included in national income.
It’s Defects:
The Pigovian definition is Precise, simple and practical but it is not free from criticisms.
First, in the light of the definition put forth by Pigou, we have unnecessarily to differentiate between commodities which can and which cannot be exchanged for money. But, in actuality, there is no difference in the fundamental forms of such commodities, no matter they can be exchanged for money.
Second, according to this definition when only such commodities as can be exchanged for money are included in estimation of national income the national income cannot be correctly measured. According to Pigou, a woman’s services as a nurse would be included in national income but excluded when she worked in the home to look after the children because she did not receive any salary for it.
Similarly, Pigou is of the view that if a man marries his lady secretary the national income diminishes as he has no longer to pay for her services. Thus the Pigovian definition gives rise to a number of paradoxes. Third, the Pigovian definition is applicable only to the developed countries where goods and services are exchanged for money in the market.
According to this definition, in the backward and underdeveloped countries of the world, where a major portion of the produce is simply bartered, correct estimate of national income will not be possible, because it will always work out less than the real level. The definition advanced by Pigou has a limited scope.
Fisher’s Definition:
Fisher adopted ‘consumption’ as the criterion of national income whereas Marshall and Pigou regarded it to be production. According to Fisher, “The national dividend or income consists solely of services as received by ultimate consumers, whether from their material or from the human environments. Thus a piano or an overcoat made for me this year is not a part of this year’s income, but an addition to the capital. Only the rendered to me during this year by these things are income.”
Fisher’s definition is considered to be better than that of Marshall or Pigou, because Fisher’s definition provides an adequate concept of economic welfare which is dependent on consumption and consumption represents our standard of living.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
It’s Defect:
But from the practical point of view, this definition is less useful, because there are certain difficulties in measuring the goods and services in terms of money.
First, it is more difficult to estimate the money value of net consumption than that of net production. In one country there are several individuals who consume a particular good and that too at different places and, therefore, it is very difficult to estimate their total consumption in terms of money.
Second, certain consumption goods are durable and last for many years. If we consider the example of piano or overcoat, as given by Fisher, only the services rendered to us during one year by them will be included in income.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
If an overcoat costs Rs 100 and lasts for ten years, Fisher will take into account only Rs 10 as national income during one year, whereas Marshall and pigou will include Rs 100 in the national income for the year when it is made. Besides, it cannot be said with certainty that the overcoat will last only for ten years. It may last longer or for short period.
Third the durable goods generally keep changing hands leading to a change in their ownership and value too. It, therefore, becomes difficult to measure in money the service-value of these goods from the point of view of consumption.
For instance, the owner of a Maruti sells it at a price higher than its real price and the purchaser after using it for a number of years, further sells it at its actual price. Now the question is as to which of its price, whether actual or black market one, should we take into account, and afterwards when it is transferred from one person to another, which of its value according to its average age should be included in national income?
Conclusion:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
But the definition advanced by Marshall, Pigou and Fisher are not altogether flawless. However, the Marshallian and Pigovian definitions tell us of the reasons influencing economic welfare, whereas Fisher’s definition helps us compare economic welfare in different years.
From the modern point of view, Simon Kuznets has defined national income as the net output of commodities and services flowing during the year from the country’s productive system in the hands of the ultimate consumers.
On the other hand, in one of the reports of United Nations, national income has been defined on the basis of the systems of estimating national income, as net national product, as addition to the shares of different factors, and as net national expenditure in a country in a year’s time.
In practice while estimating national income, any of these three definitions may be adopted, because the same national income would be derived, if different items were correctly included in the estimate.
Essay # 2. Concepts of National Income:
There are number of concepts pertaining to national income and methods of measurement relating to national income. They are discussed below.
1. Gross Domestic Product (GDP):
GDP is the total value of goods and services produced within the country during a year. This is calculated at market prices and is known as GDP at market prices. Dernberg defines GDP at market price as “the market value of the output of final goods and services produced in the domestic territory of a country during an accounting year.”
ADVERTISEMENTS:
There are three different ways to measure GDP:
Product Method, Income Method and Expenditure Method. These three methods of calculating GDP yield the same result because National Product = National Income = National Expenditure.
a. The Product Method:
In this method, the value of all goods and services produced in different industries during the year is added up. This is also known as the Value Added Method to GDP or GDI at Factor Cost by Industry of Origin.
The following items are included in India in this: agriculture and allied services; mining; manufacturing, construction, electricity, gas and water supply; transport, communication and trade; banking and insurance, real estates and ownership of dwellings and business services; and public administration and defence and other services (or government services). In other words, it is the sum of Gross Value Added.
b. The Income Method:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The people of a country who produce GDP during a year receive incomes from their work. Thus GDP by income method is the sum of all factor incomes: Wages and Salaries (compensation of employees) + Rent + Interest + Profit.
c. Expenditure Method:
This method focuses on goods and services produced within the country during one year.
GDP by expenditure method includes:
(1) Consumer expenditure on services and durable and non-durable goods (C),
(2) Investment in fixed capital such as residential and non-residential building, machinery, and inventories (I),
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(3) Government expenditure on final goods and services (G),
(4) Export of goods and services produced by people of the country (X),
(5) Less imports (M). That part of consumption, investment and government expenditure which is spent on imports is subtracted from GDP. Similarly, any imported component, such as raw material, which is used in the manufacture of export goods, is also excluded.
Thus GDP by expenditure method at market prices = C + I + G + (X – M), where (X – M) is net export which can be positive or negative.
2. GDP at Factor Cost:
GDP at factor cost is the sum of net value added by all producers within the country. Since the net value added gets distributed as income to the owners of factors of production, GDP is the sum of domestic factor incomes and fixed capital consumption (or depreciation).
Thus GDP at Factor Cost = Net value added + Depreciation.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
GDP at factor cost includes:
(i) Compensation of Employees i.e., wages, salaries, etc.
(ii) Operating Surplus which is the business profit of both incorporated and unincorporated firms,
(iii) Mixed Income of Self- employed.
Conceptually, GDP at factor cost and GDP at market price must be identical. This is because the factor cost (payments to factors) of producing goods must equal the final value of goods and services at market prices. However, the market value of goods and services is different from the earnings of the factors of production.
In GDP at market price are included indirect taxes and are excluded subsidies by the government. Therefore, in order to arrive at GDP at factor cost, indirect taxes are subtracted and subsidies are added to GDP at market price.
Thus, GDP at Factor Cost = GDP at Market Price – Indirect Taxes + Subsidies.
3. Net Domestic Product (NDP):
NDP is the value of net output of the economy during the year. Some of the country’s capital equipment wears out or becomes obsolete each year during the production process. The value of this capital consumption is some percentage of gross investment which is deducted from GDP. Thus Net Domestic Product = GDP at Factor Cost – Depreciation.
4. Nominal and Real GDP:
When GDP is measured on the basis of current prices, it is called GDP at current prices or nominal GDP. On the other hand, when GDP is calculated on the basis of fixed prices in some year, it is called GDP at constant prices or real GDP.
Nominal GDP is the value of goods and services produced in a year and measured in terms of rupees (money) at current (market) prices. In comparing one year with another, we are faced with the problem that the rupee is not a stable measure of purchasing power. GDP may rise a great deal in a year, not because the economy has been growing rapidly but because of rise in prices (or inflation).
On the contrary, GDP may increase as a result of fall in prices in a year but actually it may be less as compared to the last year. In both the cases, GDP does not show the real state of the economy. To rectify the underestimation and overestimation of GDP, we need a measure that adjusts for rising and falling prices. This can be done by measuring GDP at constant prices which is called real GDP.
To find out the real GDP, a base year is chosen when the general price level is normal, i.e., it is neither too high nor too low. The prices are set to 100 (or 1) in the base year. Now the general price level of the year for which real GDP is to be calculated is related to the base year on the basis of the following formula which is called the deflator index:
Real GDP = GDP for the/Current Year × Base Year (=100)/Current Year Index. Suppose 1990-91 is the base year and GDP for 1999-2000 is Rs. 6, 00,000 crores and the price index for this year is 300.
Thus, Real GDP for 1999-2000 = Rs. 6, 00,000 × 100/300 = Rs. 2, 00,000 crores.
5. GDP Deflator:
GDP deflator is an index of price changes of goods and services included in GDP. It is a price index which is calculated by dividing the nominal GDP in a given year by the real GDP for the same year and multiplying it by 100. Thus,
GDP Deflator = Nominal (or Current Prices) GDP/Real (or Constant Prices) GDP x 100
For example, GDP Deflator in 1997-98 = 1426.7th. crores/1049.2th. crores at x 100= 135.9
993 – 94 prices
It shows that at constant prices (1993-94), GDP in 1997-98 increased by 135.9% due to inflation (or rise in prices) from Rs. 1049.2 thousand crores in 1993-94 to Rs. 1426.7 thousand crores in 1997-98.
6. Gross National Product (GNP):
GNP is the total measure of the flow of goods and services at market value resulting from current production during a year in a country, including net income from abroad.
GNP includes four types of final goods and services:
(1) Consumers’ goods and services to satisfy the immediate wants of the people;
(2) Gross private domestic investment in capital goods consisting of fixed capital formation, residential construction and inventories of finished and unfinished goods;
(3) Goods and services produced by the government; and
(4) Net export of goods and services, i.e., the difference between value of exports and imports of goods and services, known as net income from abroad.
In this concept of GNP, there are certain factors that have to be taken into consideration.
First, GNP is the measure of money, in which all kinds of goods and services produced in a country during one year are measured in terms of money at current prices and then added together. But in this manner, due to an increase or decrease in the prices, the GNP shows a rise or decline, which may not be real.
To guard against erring on this account, a particular year (say for instance 1980) when prices are normal is taken as the base year and the GNP is adjusted in accordance with the index number for that year. This will be known as GNP at 1980 prices or at constant prices.
Second, in estimating GNP of the economy, the market price of only the final products should be taken into account. Many of the products pass through a number of stages before they are ultimately purchased by consumers.
If those products were counted at every stage, they would be included many a time in the national product. Consequently, the GNP would increase too much. To avoid double counting, therefore, only the final products and not the intermediary goods should be taken into account.
Third, goods and services rendered free of charge are not included in the GNP because it is not possible to have a correct estimate of their market prices. For example, the bringing up of a child by the mother, imparting instructions to his son by a teacher, recitals to his friends by a musician, etc.
Fourth the transactions which do not arise from the produce of current year or which do not contribute in any way to production are not included in the GNP. The sale and purchase of old goods; and of shares, bonds and assets of existing companies are not included in GNP because these do not make any addition to the national product, and the goods are simply transferred.
Likewise, the payments received under social security, e.g., unemployment insurance allowance, old age pension, and interest on public loans are also not included in GNP, because the recipients do not provide any service in lieu of them. But the depreciation of machines, plants and other capital goods is not deducted from GNP
Fifth the profits earned or losses incurred on account of changes in capital assets as a result of fluctuations in market prices are not included in the GNP if they are not responsible for current production or economic activity. For example, if the price of a house or a piece of land increases due to inflation, the profit earned by selling it will not be a part of GNP.
But if, during the current year, a portion of a house is constructed anew, the increase in the value of the house (after subtracting the cost of the newly constructed portion) will be included in the GNP. Similarly, variations in the value of assets, that can be ascertained beforehand and are insured against flood or fire, are not included in the GNP.
Last, the income earned through illegal activities is not included in the GNP. Although the goods sold in the black-market are priced and fulfil the needs of the people, but as they are not useful from the social point of view, the income received from their sale and purchase is always excluded from the GNP.
But there are two main reasons for this. One, it is not known whether these things were produced during the current year or the preceding years. Two, many of these goods are foreign made and smuggled and hence not included in the GNP.
Three Approaches to GNP:
After having studied the fundamental constituents of GNP, it is essential to know how it is estimated. Three approaches are employed for this purpose. One, the income method to GNP; two, the expenditure method to GNP; and three, the value added method to GNP Since gross income equals gross expenditure, GNP estimated by all these methods would be the same with appropriate adjustments.
a. Income Approaches to GNP:
The income approach to GNP consists of the remuneration paid in terms of money to the factors of production annually in a country.
Thus GNP is the sum total of the following items:
(i) Wages and Salaries:
Under this head fall all forms of wages and salaries earned through productive activities by workers and entrepreneurs. It includes all sums received or deposited during a year by way of all types of contributions like overtime, commission, provident fund, insurance, etc.
(ii) Rents:
Total rent includes the rents of land, shop, house, factory, etc. and the estimated rents of all such assets as are used by the owners themselves.
(iii) Interest:
Under interest comes the income by way of interest received by the individual of a country from different sources. To this is added, the estimated interest on that private capital which is invested and not borrowed by the businessman in his personal business. But the interest received on governmental loans has to be excluded, because it is a mere transfer of national income.
(iv) Dividends:
Dividends earned by the shareholders from companies are included in the GNP.
(v) Mixed incomes:
These include profits of unincorporated business, self-employed persons and partnerships. They form part of GNP.
(vi) Undistributed corporate profits:
Profits which are not distributed by companies and are retained by them are included in the GNP.
(vii) Mixed incomes:
These include profits of unincorporated business, self-employed persons and partnerships. They form part of GNP
(viii) Direct taxes:
Taxes levied on individuals, corporations and other businesses are included in the GNP.
(ix) Indirect taxes:
The government levies a number of indirect taxes, like excise duties and sales tax. These taxes are included in the prices of commodities. But revenue from these goes to the government treasury and not to the factors of production. Therefore, the income due to such taxes is added to the GNP.
(x) Depreciation:
Every corporation makes allowance for expenditure on wearing out and depreciation of machines, plants and other capital equipment. Since this sum also is not a part of the income received by the factors of production, it is, therefore, also included in the GNP.
(xi) Net income earned from Abroad:
This is the difference between the value of exports of goods and services and the value of imports of goods and services. If this difference is positive, then it is added to the GNP and if it is negative it is deducted from the GNP.
Thus GNP according to the Income Method = Wages and Salaries + Rents + Interest + Dividends + Undistributed Corporate Profits +Mixed Incomes +Direct Taxes+ Indirect Taxes+ Depreciation+ Net Income from abroad.
b. Expenditure approach to GNP:
From the expenditure view point, GNP is the sum total of expenditure incurred on goods and services during one year in a country.
It includes the following items:
(i) Private consumption expenditure:
It includes all types of expenditure on personal consumption by the individuals of a country. It comprises expenses on durable goods like watch, bicycle, radio, etc.; expenditure on single-use consumers’ goods like milk, bread, ghee, clothes etc., as also the expenditure incurred on services of all kinds like fees for school, doctor, lawyer and transport. All these are taken as final goods.
(ii) Gross domestic private investment:
Under this comes, the expenditure incurred by private enterprise on new investment and on replacement of old capital. It includes expenditure on house construction, factory- buildings, and all types of machinery, plants and capital equipment. In particular, the increase or decrease in the inventory is added to or subtracted from it.
The inventory includes produced but unsold manufactured and semi-manufactured goods during the year and the stocks of raw material, which have to be accounted for in GNP. It does not take into account the financial exchange of shares and stocks because their sale and purchase is not real investment. But depreciation is added.
(iii) Net foreign investment:
It means the difference between exports and imports of export surplus. Every country exports to or imports from certain foreign countries. The imported goods are not produced within the country and hence cannot be included in national income, but the exported goods are manufactured within the country. Therefore, the difference of value between exports (X) and imports (M), whether positive or negative, is included in the GNP.
(iv) Government expenditure on goods and services:
The expenditure incurred by the government on goods and services is a part of the GNP. Central, State or Local governments spend a lot on their employees, police and army. To run the offices, the governments have also to spend on contingencies which include paper, pen, pencil and various types of stationery, cloth, furniture, cars, etc.
It also includes the expenditure on government enterprises. But expenditure on transfer payments is not added, because these payments are not in exchange for goods and services produced during the current year.
Thus GNP according to the Expenditure Method=Private Consumption Expenditure (C) + Gross Domestic Private Investment (1) + Net Foreign Investment (X – M) + Government Expenditure on Goods and Services (G) = C + I + (X – M) + G. As already pointed out above, GNP estimated by either the income or the expenditure method would work out to be the same, if all the items are correctly calculated.
c. Value added approach to GNP:
Another method of measuring GNP is by value added. In calculating GNP, the money value of final goods and services produced at current prices during a year is taken into account. This is one of the ways to avoid double counting.
But it is difficult to distinguish properly between a final product and an intermediate product. For instance, raw materials, semi-finished products, fuels and services, etc. are sold as inputs by one industry to the other. They may be final goods for one industry and intermediate for others.
So, to avoid duplication, the value of intermediate products used in manufacturing final products must be subtracted from the value of total output of each industry in the economy. Thus the difference between the value of material outputs and inputs at each stage of production is called the value added.
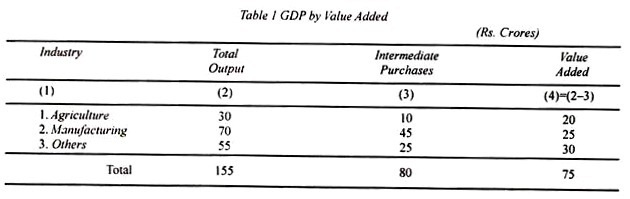
If all such differences are added up for all industries in the economy, we arrive at the GNP by value added. GNP by value added = Gross Value added + net income from abroad. Its calculation is shown in Table 1.
The Table is constructed on the supposition that the entire economy for purposes of total production consists of three sectors. They are agriculture, manufacturing, and others, consisting of the tertiary sector. Out of the value of total output of each sector is deducted the value of its intermediate purchases (or primary inputs) to arrive at the value added for the entire economy.
Thus the value of total output of the entire economy as per Table 1 is Rs 155 crores and the value of its primary inputs comes to Rs 80 crores. Thus the GNP by value added is Rs 75 crores (Rs 155minus Rs. 80 crores).
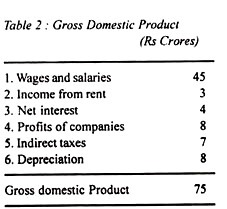
The total value added equals the value of gross national (domestic) product of the economy. Out of this value added, the major portion goes in the form of wages and salaries, rent, interest and profits, a small portion goes to the government as indirect taxes and the remaining amount is meant for depreciation. This is shown in Table 2.
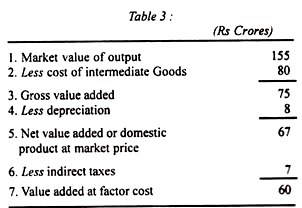
Thus we find that the total gross value added of an economy equals the value of its gross domestic product. If depreciation is deducted from the gross value added, we have net value added which comes to Rs 67 crores (Rs 75 minus 8 crores). This is nothing but net domestic product at market prices.
Again, if indirect taxes (Rs 7 crores) are deducted from the net domestic product of Rs 67 crores, we get Rs 60 crores as the net value added at factor cost which is equivalent to net domestic product at factor cost. This is illustrated in Table 3.
This value added at factor cost is equal to the net domestic product at factor cost, as given by the total of items 1 to 4 of Table 46.2 (Rs 45 + 3 + 4 + 8 crores = Rs 60 crores). If we add net income received from abroad to the gross value added, this gives us gross national income. Suppose net income from abroad is Rs 5 crores. Then the gross national income is Rs 80 crores (Rs 75 crores + Rs 5 crores).
Its Importance:
The value added method for measuring national income is more realistic than the product and income methods because it avoids the problem of double counting by excluding the value of intermediate products. Thus this method establishes the importance of intermediate products in the national economy.
Second, by studying the national income accounts relating to value added, the contribution of each production sector to the value of the GNP can be found out.
For instance, it can tell us whether agriculture is contributing more or the share of manufacturing is falling, or of the tertiary sector is increasing in the current year as compared to some previous years. Third, this method is highly useful because “it provides a means of checking the GNP estimates obtained by summing the various types of commodity purchases.”
Its Difficulties:
However, difficulties arise in the calculation of value added in the case of certain public services like police, military, health, education, etc. Which cannot be estimated accurately in money terms? Similarly, it is difficult to estimate the contribution made to value added by profits earned on irrigation and power projects.
7. GNP at Market Prices:
When we multiply the total output produced in one year by their market prices prevalent during that year in a country, we get the Gross National Product at market prices. Thus GNP at market prices means the gross value of final goods and services produced annually in a country plus net income from abroad. It includes the gross value of output of all items from (1) to (4) mentioned under GNP.
GNP at Market Prices = GDP at Market Prices + Net Income Earned from Abroad.
8. GNP at Factor Cost:
GNP at factor cost is the sum of the money value of the income produced by and accruing to the various factors of production in one year in a country. It includes all items mentioned above under Income Approach to GNP less indirect taxes.
GNP at market prices always includes indirect taxes levied by the government on goods which raise their prices. But GNP at factor cost is the income which the factors of production receive, in return, for their services alone. It is the cost of production. Thus GNP at market prices is always higher than GNP at factor cost.
Therefore, in order to arrive at GNP at factor cost, we deduct indirect taxes from GNP at market prices. Again, it often happens that the cost of production of a commodity to the producer is higher than price of a similar commodity in the market.
In order to protect such producers, the government helps them by granting monetary help in the form of a subsidy equal to the difference between the market price and the cost of production of the commodity.
As a result, the price of the commodity to the producer is reduced and equals the market price of similar commodity. For example, if the market price of rice is Rs 3 per kg but it costs the producers in certain areas Rs 3.50.
The government gives a subsidy of 50 paise per kg to them in order to meet their cost of production. Thus in order to arrive at GNP at factor cost, subsidies are added to GNP at market prices. GNP at Factor Cost = GNP at Market Prices-Indirect Taxes + Subsidies.
9. Net National Product (NNP):
GNP includes the value of total output of consumption goods and investment goods. But the process of production uses up a certain amount of fixed capital. Some fixed equipment wears out, its other components are damaged or destroyed, and still others are rendered obsolete through technological changes.
All this process is termed depreciation or capital consumption allowance. In order to arrive at NNP, we deduct depreciation from GNP. The word ‘net’ refers to the exclusion of that part of total output which represents depreciation. Thus NNP= GNP-Depreciation.
10. NNP at Market Prices:
Net National Product at market prices is the net value of final goods and services evaluated at market prices in the course of one year in a country. If we deduct depreciation from GNP at market prices, we get NNP at market prices. Thus NNP at Market Prices=GNP at Market Prices-Depreciation.
11. NNP at Factor Cost:
Net National Product at factor cost is the net output evaluated at factor prices. It includes income earned by factors of production through participation in the production process such as wages and salaries, rents, profits, etc. It is also called National Income. This measure differs from NNP at market prices in that indirect taxes are deducted and subsidies are added to NNP at market prices in order to arrive at NNP at factor cost. Thus:
NNP at Factor Cost = NNP at Market Prices-Indirect taxes + Subsidies.
= GNP at Market Prices-Depreciation-Indirect taxes + Subsidies.
= National Income.
Normally, NNP at market prices is higher than NNP at factor cost because indirect taxes exceed government subsidies. However, NNP at market prices can be less than NNP at factor cost when government subsidies exceed indirect taxes.
12. Domestic Income:
Income generated (or earned) by factors of production within the country from its own resources is called domestic income or domestic product.
Domestic income includes:
(i) Wages and salaries,
(ii) Rents, including imputed house rents,
(iii) Interest,
(iv) Dividends
(v) Undistributed corporate profits, including surpluses of public undertakings,
(vi)Mixed incomes consisting of profits of unincorporated firms, self-employed persons, partnerships, etc., and
(vii) Direct taxes.
Since domestic income does not include income earned from abroad, it can also be shown as: Domestic Income=National Income-Net Income earned from abroad. Thus the difference between domestic income and national income is the net income earned from abroad.
If we add net income from abroad to domestic income, we get national income, i.e., National Income = Domestic Income + Net Income earned from abroad. But the net national income earned from abroad may be positive or negative. If exports exceed imports, net income earned from abroad is positive.
In this case, national income is greater than domestic income. On the other hand, when imports exceed exports, net income earned from abroad is negative and domestic income is greater than national income.
13. Private Income:
Private income is income obtained by private individuals from any source, productive or otherwise, and the retained income of corporations. It can be arrived at from NNP at Factor Cost by making certain additions and deductions.
The additions include transfer payments such as pensions, unemployment allowances, and sickness and other social security benefits, gifts and remittances from abroad, windfall gains from lotteries or from horse racing, and interest on public debt.
The deductions include income from government departments as well as surpluses from public undertakings, and employees’ contribution to social security schemes like provident funds, life insurance, etc. Thus Private Income= National Income (or NNP at Factor Cost) +Transfer Payments+ Interest on Public Debt-Social Security-Profits and Surpluses of Public Undertakings.
14. Personal Income:
Personal income is the total income received by the individuals of a country from all sources before payment of direct taxes in one year. Personal income is never equal to the national income, because the former includes the transfer payments whereas they are not included in national income.
Personal income is derived from national income by deducting undistributed corporate profits, profit taxes, and employees’ contributions to social security schemes.
These three components are excluded from national income because they do reach individuals. But business and government transfer payments, and transfer payments from abroad in the form of gifts and remittances, windfall gains, and interest on public debt which are a source of income for individuals are added to national income.
Thus Personal Income=National Income-Undistributed Corporate Profits-Profit Taxes-Social Security Contribution + Transfer Payments + Interest of Public Debt. Personal income differs from private income in that it is less than the latter because it excludes undistributed corporate profits. Thus Personal income = Private Income-Undistributed Corporate Profits-Profit Taxes.
15. Disposable Income:
Disposable income or personal disposable income means the actual income which can be spent on consumption by individuals and families. The whole of the personal income cannot be spent on consumption, because it is the income that accrues before direct taxes have actually been paid. Therefore, in order to obtain the disposable income, direct taxes are deducted from personal income.
Thus Disposable income=Personal Income-Direct Taxes. But the whole of the disposable income is not spent on consumption and a part of it is saved. Therefore, the disposable income is divided into consumption expenditure and saving. Thus Disposable Income = Consumption Expenditure+ Savings.
If disposable income is to be deduced from national income, we deduct indirect taxes plus subsidies, direct taxes on personal and on business, social security payments, undistributed corporate profits or business savings from it and add transfer payments and net income from abroad to it.
Thus Disposable Income=National Income-Business Savings-Indirect Taxes plus Subsidies-Direct Taxes on Persons-Direct Taxes on Business-Social Security Payments+ Transfer Payments + Net Income from Abroad.
16. Real Income:
Real income is national income expressed in terms of a general level of prices of a particular year taken as base. National income is the value of goods and services produced as expressed in terms of money at current prices.
But it does not indicate the real state of the economy. It is possible that the net national product of goods and services this year might have been less than that of the last year, but owing to an increase in prices, the NNP might be higher this year.
On the contrary, it is also possible that NNP might have increased but the price level might have fallen, as a result of which national income would appear to be less than that of the last year. In both the situations, the national income does not depict the real state of the country. To rectify such as a mistake, the concept of real income has been evolved.
In order to find out the real income of a country, a particular year is taken as the base year when the general price level is neither too high nor too low and the price level for that year is assumed to be 100. Now that general level of prices of the given year for which the national income (real) is to be determined is assessed in accordance with the prices of the base year. For this purpose the following formula is employed.
Real NNP = NNP for the Current Year x Base Year Index (= 100)/Current Year Index.
Suppose 1993-94 is the base year and the national income for 2004-05 is Rs 20,000 crores and the index 100 number for this year is 250. Hence, Real National Income for 2004-05=20,000x Rs. 8,000 crores. This is also known as National Income at Constant Prices.
17. Per Capita Income:
The average income of the people of a country in a particular year is called Per Capita Income for that year. This concept also refers to the measurement of income at current prices and at constant prices. For instance, in order to find out the per capita income for 2005, at current prices, the national income of a country is divided by the population of the country in that year
Per Capita Income for 2005 = National income for 2005/Population in 2005
Similarly, for the purpose of arriving at the Real Per Capita Income, this very formula is employed.
Real Per Capita Income for 2005 = Real national income for 2005/Population in 2005.
This concept enables us to know the average income and the standard of living of the people. But it is not very reliable, because in every country due to the unequal distribution of national income, a major portion of it goes to the richer sections of the society and thus income received by the common man is lower than the per capita income.
Essay # 3. Methods of Measuring National Income:
There are four methods of measuring national income. Which method is to be employed depends on the availability of data in a country and the purpose in hand.
1. Product Method:
According to this method, the total value of final goods and services produced in a country during a year is calculated at market prices.
To find out the GNP, the data of all productive activities, such as agricultural products, wood received from forests, minerals received from mines, commodities produced by industries, the contributions to production made by transport, communications, insurance companies, lawyers, doctors, teachers, etc. are collected and assessed at market prices.
Only the final goods and services are included and the intermediary goods and services are left out.
2. Income Method:
According to this method, the net income payments received by all citizens of a country in a particular year are added up, i.e., net incomes that accrue to all factors of production by way of net rents, net wages, net interest and net profits are all added together but incomes received in the form of transfer payments are not included in it.
The data pertaining to income are obtained from different sources, for instance, from income tax department in respect of high income groups and in case of workers from their wages bills.
3. Expenditure Method:
According to this method, the total expenditure incurred by the society in a particular year is added together and includes personal consumption expenditure, net domestic investment, government expenditure on goods and services, and net foreign investment. This concept is based on the assumption that national income equals national expenditure.
4. Value Added Method:
Another method of measuring national income is the value added by industries. The difference between the value of material outputs and inputs at each stage of production is the value added. If all such differences are added up for all industries in the economy, we arrive at the gross domestic product.
Essay # 4. Importance of National Income Analysis:
The national income data have the following importance.
1. For the Economy:
National income data are of great importance for the economy of a country. These days the national income data are regarded as accounts of the economy, which are known as social accounts.
These refer to net national income and net national expenditure, which ultimately equal each other Social accounts tell us how the aggregates of a nation’s income, output and product result from the income of different individuals, products of industries and transactions of international trade.
Their main constituents are inter-related and each particular account can be used to verify the correctness of any other account Based very much on social accounts, the national income data have the following importance.
2. National Policies:
National income data form the basis of national policies such as employment policy because these figures enable us to know the direction in which the industrial output, investment and savings’ etc. change, and proper measures can be adopted to bring the economy to the right path.
3. Economic Planning:
In the present age of planning, the national data are of great importance. For economic planning, it is essential that the data pertaining to a country’s gross income, output, saving and consumption from different sources should be available.
Without these, planning is not possible. Similarly, the economists propound short-run as well long-run economic models or long-run investment models in which the national income data are very widely used.
4. Economic Models:
Economists build short-run and long-run economic models in which the national income data are widely used.
5. For Research:
The national income data are also made use of by the research scholars of economics, they make use of the various data of the country’s input, output, income, saving, consumption, investment employment, etc., which are obtained from social accounts.
6. Per-Capita Income:
National income data are significant for a country’s per capita income which reflects the economic welfare of the country. The higher the per capita income, the higher the economic welfare and vice versa.
7. Distribution of Income:
National income statistics enable us to know about the distribution of income in the country. From the data pertaining to wages, rent, interest and profits we learn of the disparities in the incomes of different sections of the society.
Similarly, the regional distribution of income is revealed it is only on the basis of these that the government can adopt measures to remove the inequalities in income distribution and to restore regional equilibrium. With a view to removing these personal and regional disequilibria, the decisions to levy more taxes and increase public expenditure also rest on national income statistics.