Expansionary Fiscal Policy:
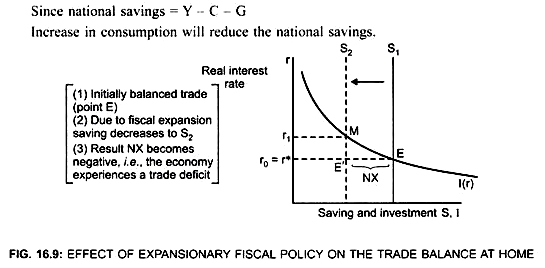
Effect of Fiscal Expansion at home in a small open economy.
Due to an expansionary fiscal policy, the economy moves from balanced trade to a trade deficit.
This is because, due to fiscal expansion, national saving (S = Y – C – G) decreases.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Result:
Net capital outflow (CF) will become negative
When CF falls, NX also falls, and thus NX becomes negative.
There exists trade deficit.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Thus, starting from a balanced trade, a change in fiscal policy that decreases national saving leads to trade deficit.
Similarly, decrease in tax will increase the disposable income
Since Yd = Y-T and C=f(Yd) or C = f(Y-T)
... Decrease in taxes will increase the consumption
Effect of Fiscal Expansion Abroad in a Small Open Economy:
In a small open economy:
An expansionary fiscal policy abroad leads to a trade surplus.
e.g. when the foreign Governments (US) increase their Government purchases; the effect of Government purchase on home country (e.g. India) trade balance will depend on whether these foreign countries are a small part or a large part of the world economy.
If the foreign country (USA) is a large part of the world economy, then an increase in the Government purchases abroad will lead to decrease in world saving and thus trade surplus at home
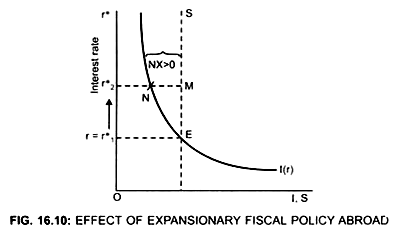
When Government purchase increases, world saving reduces because S = Y – C – G and the world interest rate will rise, figure (16.10)
Initially the economy is in equilibrium at point E.
I (r) = S
ADVERTISEMENTS:
r1* = r
Increase in the Government spending reduces savings abroad that is, world saving reduces.
As result, interest rate rises from r1* to r2*
[I > S in World economy (abroad e.g. USA)]
ADVERTISEMENTS:
In the domestic country:
Due to increase in the world interest rate (r2*> r) cost of borrowing increases, investment will decrease.
However, there will be no change in domestic saving (e.g, India)
With Saving remaining same, (due to no change in the domestic policy)
ADVERTISEMENTS:
S > I by NM at the world interest rate, r2*
Since S abroad has decreased, I > S
and S in home country has increased; S > I
... Some of the savings of the home country (India) will flow abroad (to USA)
Thus, there will be trade surplus at home in small open economy.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Initially the economy is in equilibrium at point E.
I (r) = S
r1* = r
Due to fiscal expansion abroad, world saving decreases. Therefore, world interest rate increases from r*1 to r*2
With interest rate in domestic country (India) remaining same at r = r*1
... r < r*2 (Fig. 16.10)
ADVERTISEMENTS:
As a result:
Investment abroad by home country (India) will increase, that is, Indians will find it more profitable to invest abroad.
... Investment in home country will decrease
I = r*2N
S = r*2M
S > I by NM
ADVERTISEMENTS:
... Some of savings of the home country (India) in form of investment will flow abroad (USA).
... Net Capital flow will become positive.
... There will be a trade surplus at home = NM
Conclusion:
Fiscal expansion at home leads to a trade deficit at home while fiscal expansion abroad will lead to a trade surplus at home.