Read this article to learn about the most frequently asked questions on Form of Market and Price Determination.
Q.1. What is meant by market in economics?
Ans. In economics, market refers to the entire area in which buyers and sellers of a commodity are in close contact with each other for purchase and sale of that commodity.
Q.2. In which market form are there no close substitutes of the product?
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Ans. Monopoly.
Q.3. In which market form is there a single seller?
Ans. Monopoly.
Q.4. Define monopoly.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Ans. Monopoly is a market condition in which there is a single seller/producer of a product having no close substitutes.
Q.5. Define Oligopoly.
Ans. A form of imperfect competition in which a small number of big firms produce majority of the total output of the industry and are mutually dependent for taking price and output decisions.
Q.6. Under which market form, a firm is a price-taker?
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Ans. Perfect competition.
Q.7. When is a firm called ‘price taker?
Ans. The firm is called price taker when it has to adopt the price determined by market demand and market supply.
Q.8. What is a price taker firm?
Ans. A price taker firm is a firm which has no option but to sell at a price determined at the industry level.
Q.9. When is a firm called ‘price maker’?
Ans. When the firm can influence the market price of the product that the firm is producing.
Q.10. What is a price maker firm?
Ans. A price maker firm is one which can influence the market price of the product on its own.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Q.11. In which market form are the products homogeneous?
Ans. Perfect competition.
Q.12. In which market form demand curve of a firm is perfectly elastic?
Ans. Perfect competition.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Q.13. In which market form can a firm not influence the price of the product?
Ans. Perfect competition.
Q.14. Under which market form a firm’s marginal revenue is always equal to price?
Ans. Perfect competition.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Q.15. In which market form are the average and marginal revenue of a firm always equal?
Ans. Perfect competition.
Q.16. What is a cartel?
Ans. A group of large number of firms which explicitly and openly agree to work together is called a cartel.
Q.17. How many firms are there in a monopoly market?
Ans. There is a single seller in a monopoly market.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Q.18. In which market form are products differentiated?
Ans. Monopolistic competition.
Q.19. What can you say about the number of buyers and sellers under monopolistic competition?
Ans. In this market form, there are a large number of buyers and sellers.
Q.20. State one feature of oligopoly.
Ans. (1) Few firms.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(2) Firms are interdependent in taking price and output decisions.
(3) Barriers to the entry of firms
(4) Non-Price competition.
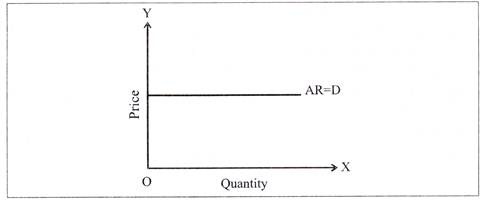
Q.21. Draw average revenue curve of a firm under perfect competition.
OR
Draw demand curve of a firm under perfect competition.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Ans.
Q.22. In which market form, are there restrictions on the entry of new firms?
Ans. Monopoly.
Q. 23.Define patent rights.
Ans. The owners of patent rights have exclusive rights for a production process to the extent no one else can use that technology without a hence or permission from them.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Q.24.Define persuasive advertising.
Ans. In persuasive advertising, attempt is made to persuade a consumer to buy products of the firm.
Q.25. State one characteristic of a perfectly competitive market.
Ans. Large number of buyers and sellers.
Q.26. Name the characteristic which makes monopolistic competition different from perfect competition.
Ans. Firms produce differentiated products.
Q. 27.What are selling costs?
Ans. Costs incurred on promoting the demand for a product are known as selling costs.
Q.28. What is meant by super normal profit?
Ans. Profit earned in excess of normal profit is called super normal profit.
Q.29. What is meant by normal profit?
Ans. Normal profit is the minimum profit which a firm must earn to continue to remain in business.
Q.30. What is patent life?
Ans. The number of years for which patents are valid is called patent life
Q.31. What is information advertising?
Ans. Information advertising is used to inform the consumers about new products, prices, quality etc.
Q.32. What is equilibrium price?
Ans. Equilibrium price is that price at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied of a commodity are equal.
Q.33. What is meant by equilibrium quantity?
Ans. The quantity of a commodity bought or sold at the equilibrium price, is called equilibrium quantity.
Q.34. What is market equilibrium.
Ans. The situation where market demand equals market supply and determines an equilibrium price is known as market equilibrium.
Q.35. What happens to equilibrium price of a good when the demand for that good increases?
Ans. In case of increase in demand, the equilibrium price will also increase.
Q.36. What happens to the equilibrium price when supply of a good increases?
Ans. The equilibrium price will decrease if the supply of a good increases.
Q.37. When will an increase in demand result in an increase in price but no change in quantity?
Ans. If supply of a commodity is perfectly inelastic, increase in demand will result in an increase in price only, the equilibrium quantity will remain unchanged.
Q.38. When will an increase in demand imply an increase in quantity demanded but no change in price?
Ans. If supply curve of a commodity is perfectly elastic, an increase in demand will increase the quantity demanded only there will be no effect on equilibrium price of the commodity.
Q.39. When will an increase in supply lead to a decrease in price only, but no change in quantity?
Ans. An increase in supply will lead to a decrease in equilibrium price only when demand for the commodity is perfectly inelastic.
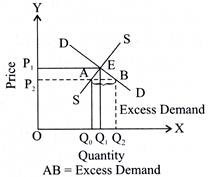
Q.40. At what price, higher or lower than the equilibrium price, will there be excess demand?
Ans. Excess demand always exists when the price is lower than the equilibrium price.
Q.41. When will an increase in supply not affect the equilibrium price?
Ans. An increase in supply will not affect the equilibrium price when demand of the commodity is perfectly elastic.
Q.42. If the demand of a commodity decreases but supply remains constant, what will be the effect on price and quantity?
Ans. Equilibrium price as well as quantity bought and sold will fall in case of decrease in demand with supply remaining constant.
Q.43. Give the meaning of excess demand of a product.
Ans. When demand for a commodity is greater than its supply at a given price, it is known as excess demand.
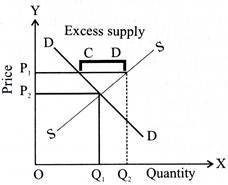
Q.44. Give meaning of excess supply of a product.
Ans. When supply of a commodity is more than its demand at a given price, it is known as excess supply.
Q.45. What happens if the market price is more than equilibrium price?
Ans. If market price is more than the equilibrium price there will be excess supply of the commodity and competition among sellers will bring down the market price to the equilibrium price.
Q.46. What is the condition for determination of equilibrium price?
Ans. Equality of quantity demanded and quantity supplied is the condition for determination of equilibrium price.
Q.47. What happens when government fixes the price of any commodity below the equilibrium price?
Ans. When the government fixes the price of any commodity at lower level than its equilibrium price, the excess demand leads to black marketing i.e. goods are illegally sold at higher price than the price fixed by the government.
Q.48. What is the aim of price control policy of the government?
Ans. The aim of price control is to keep the market price below the equilibrium price to protect the interest of the consumers.
Q.49. How does an increase in input price for a product affect its equilibrium quantity exchanged in a market?
Ans. Increase in input price will increase the cost of production and decrease the supply of the commodity, which will lead to decrease in the quantity exchanged.
Q.50. How does a favourable change in taste affect the equilibrium quantity exchanged in the market?
Ans. A favourable change in taste will increase the demand for a commodity & thus it will lead to increase in equilibrium price and quantity exchanged.
Q.51. How does an increase in the price of a substitute good affect the equilibrium price?
Ans. Increase in prices of substitute of a commodity will increase the demand increase the equilibrium price of the commodity.
Q.52. How does technological progress affect the market price and quantity exchanged?
Ans. An advanced technology will cause marginal cost to fall which will further increase the supply that will shift supply curve towards right and cause equilibrium price to fall and equilibrium quantity to rise.
Q.53. How does an increase in excise tax rate affect the market price and quantity exchanged?
Ans. An increase in excise tax rate will reduce the quantity supplied that will increase the price of the commodity.
Q.54. What IS the relationship between maximum control price and the equilibrium price?
Ans. Maximum control price is always lower than the equilibrium price.
Q.55. What is the relationship between minimum support price and equilibrium?
Ans. Minimum Support price is always fixed at higher level than the equilibrium price.
Q.56. Can the equilibrium price change?
Ans. Yes, the equilibrium price of a commodity can change when there is a change in demand and/or supply.
Q.57. What is the minimum acceptable price to a producer?
Ans. The minimum acceptable price to a producer is equal to marginal cost of production.
Q. 58. “If demand and supply both increase, equilibrium price will remain same”. Do you agree with the statement?
Ans. No, depending upon the proportion of increase in demand and supply, equilibrium price may increase, decrease or remain constant.
Example:
Ans. When increase in demand is more than increase in supply equilibrium price will rise.
When increase in demand is less than increase in supply, equilibrium price will fall.
When increase in demand is equal to increase in supply, equilibrium price will remain unchanged.
Q.59. What will happen to equilibrium price when demand is perfectly elastic and supply increases?
Ans. The equilibrium price will not be affected if demand is perfectly elastic and supply increases.
Q.60. What is the maximum price a consumer will be willing to pay for a commodity?
Ans. The maximum price a consumer will be willing to pay for a commodity is equal to the marginal utility of that commodity.
Q.61. Which factor is more active in determining the price in very short period?
Ans. Demand is more active in determining price of a commodity in very short period.
Q.62. Which factor is more active in determining the price in the long run?
Ans. Supply is more active in determining the price of a commodity in the long run.
Q.63. What will happen to equilibrium price, if both demand and supply increase in the same proportion?
Ans. The equilibrium price will remain unchanged.
Q.64. What will happen to equilibrium price, when increase in demand is more than the increase in supply?
Ans. The equilibrium price will rise.
Q.65. What will be the effect on equilibrium price if increase in demand is less than the increase in supply?
Ans. The equilibrium price will fall.
Q.66. What will be the effect on equilibrium quantity, if both demand and supply decrease in the same proportion?
Ans. The equilibrium quantity will fall.
Q.67. When does a new firm get attracted to an industry?
Ans. If an industry is earning super normal profits in the short run, new firms get attracted to that industry.
Q.68. Why do super normal profits get wiped away in the long run?
Ans. Entry of new firms in the industry increases the supply of a commodity, which leads to reduction of its price and hence the super normal profits are wiped away in the long run.
Q.69. How long does the entry/exit of firms take place in the long run?
Ans. The entry and exit of firms will keep on taking place till all firms earn normal profits.
Q.70. If the firms are earning abnormal profit, how will the number of firms in the industry change?
Ans. The number of firms in the industry will increase.
Q.71. If the firms are making abnormal losses, how will the number of firms in the industry change?
Ans. The number of firms in the industry will decrease.
Q.72. Under which market form is a firm price maker.
Ans. Monopoly.
Q.73. Will the monopolist firm continue to produce in the long run if a loss is incurred at the best short run level of output?
Ans. The monopoly firm which incurs losses at the best short run will stop producing in the long run anyway.
Q.74. When do we say there is excess demand for a commodity in the market?
Ans. When quantity demanded for a commodity exceeds the quantity supplied at a given price, it is called as situation of excess demand.
Q.75. When do we say there is excess supply for a commodity in the market?
Ans. When the quantity supplied of a commodity is greater than the quantity demanded for same at a given price, it is called excess supply.