The upcoming discussion will update you about the distinction between market price and normal price.
1. Very short period price and prevails at a particular time:
Market price is that price which prevails in a market on a single day or on very few days. It connotes day to day very short period equilibrium price determination.
Normal Price on the other-hand refers to the long period price determination. It is the equilibrium price determined by the forces of long-run demand and supply.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
2. In the determination of market price, demand plays an active role while supply plays passive role:
In the case of market price, the supply tends to be fixed and perfectly inelastic. Thus, the demand factor has a greater influence in effecting a change in the equilibrium market price. While in the case of normal price, the supply tends to be fairly elastic, so it has relatively a greater impact in setting an equilibrium price.
3. Fluctuating phenomenon and stable phenomenon:
Market price is a fluctuating phenomenon. It represents unstable equilibrium position of demand and supply. While Normal price, on the other-hand is a stable phenomenon. It represents stable equilibrium conditions of demand and supply. In short, market price is a temporary equilibrium price, while the long-run or normal price is a permanent equilibrium price under a given situation.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
4. Firm can earn profit, super normal profits or incur losses:
Market price may be higher than, equal to or less than the marginal cost of the firms involved. Thus, at a given market price, different firms may be earning super-normal profit, normal profit or even incurring losses, depending on their relative efficiency and cost conditions.
Normal price, on the other-hand, implies only a normal profit to the existing firms in a competitive market. Normal price = long-run marginal cost = long run average cost of the existing firms when industry is at full equilibrium position.
5. Affected by short-run or long-run dynamic forces of demand and supply:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Market price is affected by changes in the short-run forces of demand determinants. Normal price is affected by long-run dynamic forces of demand and supply determinants such as population growth, technological advancement, territorial expansion, innovation, changes in habits and preferences of consumers, pace of economic development etc.
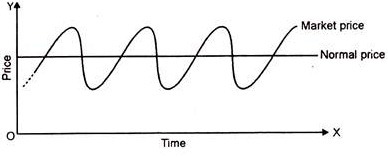
Though the market price is continually fluctuating, it is related to the normal price. It tends to oscillate around the normal price and tends to be equal to it but momentarily. The relationship between market and normal price may be described diagrammatically as shown above.
It may be seen from the diagram given that from time to time, the market price tends to oscillate, it moves up and down around the normal price. That is sometimes, it is higher than the normal price. That is sometimes, it is higher than the normal price, at other times, it may be equal to the normal price and at certain other times, it may be lower than the normal price.
It must be noted that market price and normal price are determined by the respective forces of demand and supply in the related periods i.e., the market period (very short period) and the long period. Thus, one should never think of the normal price as an average of the market prices taken over a period of time.
Thus, there is no statistical relationship between market price and normal price. Their relationship is functional based on the time element. Market price represents the very short period equality between demand and supply.
Next, market price is a reality, whereas the normal price is a myth. This is because, the actual action and market behaviour of sellers and buyers are always seen in the very short-period in the day-to-day transactions where-as the long period is just a philosophical concepts.
Long-run may be imagined but cannot be experienced in real life, whereas very short period is always actually being lived and experienced.
“Market price oscillates round the normal price.”