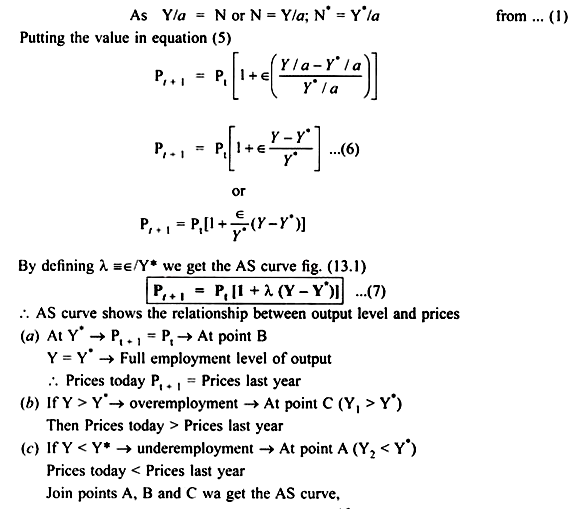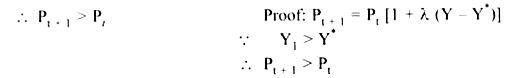The derivation of AS curve involves 4 steps:
1. Translate output to employment. – OKUN’s Law
2. Link prices charged by firms to their costs
3. Use Phillips curve relationship between wages and employment
ADVERTISEMENTS:
4. Put the three components together to derive an upward sloping AS curve
Ist Step:
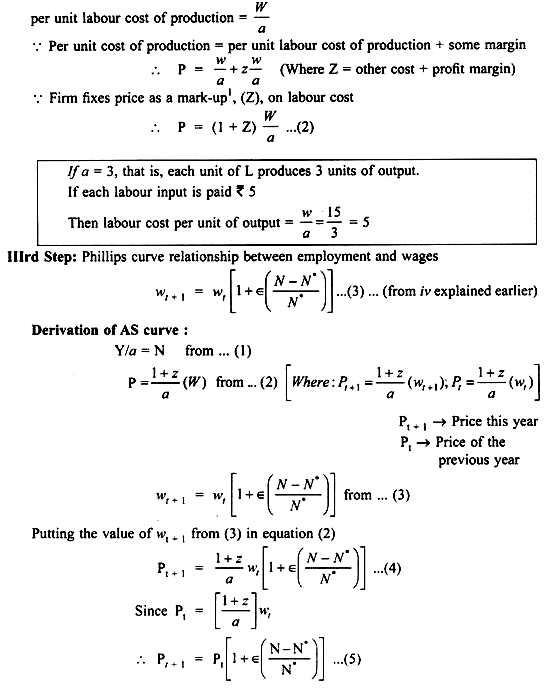
In short run, unemployment and output are closely linked. Okun’s Law states — one extra point of unemployment costs 2% of GDP Output (Y) is assumed to be proportional to the employment (N) which gives the production function [Y =f (N)].
IInd Step:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The main component of total cost is the labour cost. Firm will fix the price of output which covers its cost. Firm may want to change more than cost but the competition from existing firms and the new firms entering the industry, prevents them to hike prices.
Assume:
Firms base their price on the labour cost.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
If each unit of Labour (L) produces ‘a’ unit of output
Properties of AS curve:
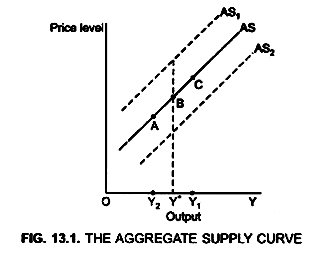
1. AS curve is upward sloping which shifts over time. Therefore, actual output differs from full employment output level
(a) If output is above full employment level
Y1 > Y* → AS curve in next period will shift upward to AS1 (Fig. 13.1)
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Actual output in current year > full employment output
Wages will increase because increase in output will lead to an increase in the demand for labour which in turn will lead to an increase in wages. As wages are the cost of production therefore increase in wages will lead to an increase in cost of production. This increase in cost will be passed on to increased prices and thus price will increase.
(b) If actual output is less than full employment level:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The positive AS curve is derived from the Phillips curve on the basis of 3 assumptions:
(i) Mark up is fixed at Z.
(ii) Output is proportional to employment.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(iii) Wages are less than fully flexible (that is, wages are rigid/sticky).
2. If AS is flat → Impact of output and employment on current wage is less, that is, wages respond less to unemployment.
3. Position of AS curve depends on last year price.