The following article will guide you about how there can be a rent element in the remuneration of any factor. Also learn about the definition of rent.
Rent Element in All Factor Incomes:
Ricardo restricted his theory of rent to the income from land only. In his opinion, rent of land arises owing to the fixed supply of land and owing to differences in fertility or situation of the different plots of land. The superior lands get a surplus income over the cost of producing crops; and this differential gain or producer’s surplus is the rent of land.
Marshall developed the Ricardian idea of rent by introducing the concept of quasi-rent. In his opinion, rent is not peculiar to land only; it may also arise in the short period in the income from machines and man-made appliances. The latter type of man-made capital goods may enjoy a surplus in the short period as their supplies, like the supply of land, remain more or less fixed in the short period; this surplus, however, disappears in the long run when the supply of these man-made appliances increases.
For this reason, Marshall describes the short-run net earnings of their man-made appliances as quasi-rent, as distance from rent proper which appears in the case of land only because of its limited supply even in the long run.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Modern writers like Mrs. Robinson and others have made a further extension of the concept of rent but in a different way. They have defined economic rent as the excess of actual earnings of a factor over its minimum supply price or transfer earnings. In this sense, rent arises not only in the income of land but also in the remuneration of any other factors (such as labour, capital and entrepreneur) on account of inelastic supply of the factor.
Let us discuss this in detail:
1. Economic rent in the income from land:
From the standpoint of the economy as a whole, the supply of land is absolutely fixed or is perfectly inelastic at all prices, and so from this point of view land has no alternative earnings and its transfer earnings are zero. For this reason, from the standpoint of the economy as a whole, the entire earnings of land represent a surplus and so can be treated as rent. But, from the point of view of an individual farmer only the surplus labour cost represents economic rent.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
2. Economic rent in wages:
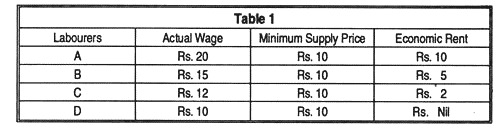
Economic rent is found in wages when the supply of labour becomes inelastic or when the demand for labour increases in relation to its supply or when labour becomes highly specific in nature. Every labourer has a minimum supply prices and economic rent arises in wages when a labourer gets something excess over this minimum supply price.
Thus, a labourer is willing to supply his labour at wages of Rs. 20 per day; but owing to an increase in the demand for labour at wages of Rs. 20 per day; but owing to an increase in the demand for labour, he gets Rs. 25 per day. Here the sum of Rs. 5 represents economic rent in his daily wages of Rs. 25. Similarly, some labourers may get rent of ability in their earnings on account of their superior abilities.
Again, there is a large element of rent in the incomes of movie stars, painters, musicians, etc. as the supply of these people in the society is relatively inelastic simply because they possess rare natural talent. In the case of a blind singer, his entire earnings may constitute economic rent as normally his transfer or alternative earnings are zero. As a general rule it can be said that the more specific the labour, the greater proportion of its earnings that consist of rent.
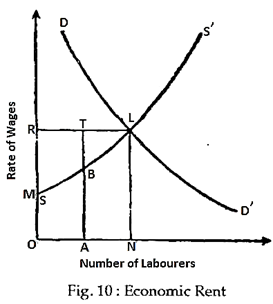
Diagrammatic Illustration:
In Fig. 10 the OA-th labourer enjoys BT economic rent in his total earnings of AT, while the ON-th labourer has no economic rent in his The total of economic rent for ON number of labourers is represented by the area RML.
3. Economic rent in interest:
Money-capital or loanable fund, like labour, has also a minimum supply price. If it gets some excess in its earnings due to a rise in its demand, the excess amount would represent economic rent in interest. In the short period the supply of some forms of loanable funds. Let us suppose that an investor is willing to lend his money-capital at the minimum supply prices of these funds may be inelastic and consequently their owners may get something excess over the minimum supply prices of these funds.
Let us suppose that an investor is willing to lend his money-capital at the minimum supply price of 12% interest, but due to a rise in the demand for money capital, he gets 16% interest. In such a case 4% excess interest represents rent element in interest or the investor’s surplus earnings.
4. Economic rent in profits:
Economic rent is also found in the income of the entrepreneur. In the short period the supply of efficient and highly skilled entrepreneurs may be limited. Owing to this reason, these entrepreneurs having superior organising abilities may earn more than normal profits. Such excess earnings over the normal profits represent rent in their incomes.
Conclusion:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Thus, it is found that there can be an element of rent in the remuneration of all factors, i.e., in wages, interest and profits. In fact the rent of land and the earnings of other factors in the short period, commonly described as quasi-rent, belong to a same broad group as all these arise due to the inelastic supply of the factor.
The supply of land is, however permanently inelastic and for this reason the surplus element in the income of land is more or less permanent, but the supply of other factors is not so fixed in the long run; it is so only in the short period. For this reason, the surplus element or rent element found in other incomes generally disappears in the long run. Accordingly, Marshall describes the rent of land as the leading species of a large genus. Thus, he observes, “The rent of land is seen, not as a thing by itself, but as the leading species of a large genus.”
Definition of Rent:
The term ‘rent’ can be defined in different ways:
(i) Ordinary meaning of rent:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
In ordinary speech the term ‘rent’ is used to mean the hire-price of land or buildings or machineries, etc. It is fixed by a contract between the owner of land or buildings and the tenant. It is called contract rent.
(ii) Ricardo’s definition:
Ricardo gives a definition of rent as used in economics. In his opinion rent is “that portion of the producer of the earth which is paid to the landlord for the use of the original and indestructible powers of the soil.”
(iii) Modern definition:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
But, the modern writers like Mrs. Robinson and others have defined economic rent as a difference between the actual earnings of a unit of a factor of production and its supply price. In other words, economic rent is a payment in excess of transfer earnings of a unit of a factor of production and its supply price. In other words, economic rent is payment in excess of transfer earnings of a particular factor. In this sense there can be an element of rent in the incomes of all factors.