This article will help you to learn about the difference between an increase and decrease in supply.
Difference between an Increase and Decrease in Supply
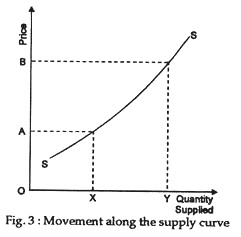
If the price of a good increases or decreases then the supplier of a good will merely move along supply curve. This means that as price increases then suppliers will supply more. See Fig. 3.
However, there could be a shift in the supply curve which is caused by changes in the conditions of supply. Normally, when we speak of an increase or decrease in supply, we are referring to a shift in the curve.
An Increase in Supply:
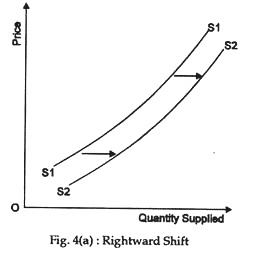
An increase in supply means that at each of the prices there is now an increase in the quantity supplied—meaning that the curve shifts to the right [Fig. 4(a)].
A Decrease in Supply:
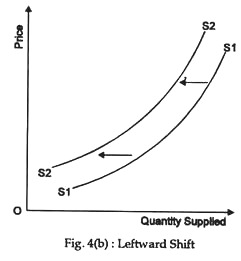
A decrease in supply means that at each of the prices there is now a decrease in quantity supplied—meaning that the curve shifts to the left [Fig. 4(b)].
Causes of Changes in Supply:
The supply of a good may change although there has been no change in price.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
There are several factors which may cause a change in supply:
1. Change in the Cost of Production:
There are various production costs involved in the production of anything, e.g., wages, rents, price of raw materials, etc. When factor prices fall it costs less to produce the same quantity. So at the old price more can be produced and supplied and the supply curve will shift to the right, and increase in costs will mean less is supplied and the supply curve shifts to the left.
2. Change in Climate:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The weather, e.g., storms, floods, is especially important to the supply of agricultural goods. A bad harvest will mean that the supply curve will shift to the left as less of the good is supplied. A good harvest will shift the supply curve to the right.
3. Technical Progress:
New inventions may improve production methods and, therefore, decrease production costs. Therefore, more can be supplied and the supply curve will shift to the right. A war might mean less technology is available and supply of some goods will drop and the curve will shift to the left.
4. Tax and Subsidies:
An increase in the taxation of a good is equivalent to an increase in its costs of production. Therefore, this may decrease supply and shift the supply curve to the left. A subsidy will tend to increase supply because it makes production cheaper. Thus the supply curve will shift to the right.