Generally, the bargaining power of employer is much higher than the bargaining power of labor.
Therefore, the employers can easily higher labor at lower wage rates.
Labor exploitation occurs when the wage paid to labor is less than the value of marginal product (VMP).
VMP can be calculated with the help of following formula:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
VMP = Physical product * sales price of product
In case of perfect competition, there is no exploitation in labor market as well as product market. This is because MRP and VMP are equal in perfect competition. Therefore, labor is getting the wage rate equal to VMP. However, the exploitation of labor exists in various other market structures, such as monopoly and monopsony. In monopoly, the exploitation of labor exists only in product market. In product market, marginal revenue is less as compared to product’s price.
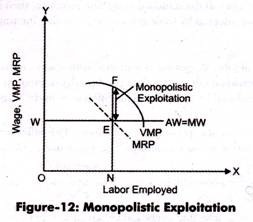
This results in the lowering down of MRP with respect to VMP. At the equilibrium point, the employer would decide the wage rate on the basis of MRP, which is already less than VMP. Therefore, the labor would get low wages than what actually he/she deserves. This leads to the exploitation of labor.
The exploitation in monopoly market is termed as monopolistic exploitation, which is shown in Figure-12:
Exploitation of labor can be prohibited by government policies and trade unions. However, monopolistic exploitation cannot be eradicated by government policies and trade unions. This is because if the trade unions compel the employers to pay high wages, then the employers are required to reduce the number of labor to make the wage rate equal to MRP.
In such a case, VMP would be more as compared to MRP, which would lead to further exploitation of labor. Therefore, the best way to remove exploitation is to make the product market work under the conditions of perfect competition. In case of monopsonistic competition, government and trade unions strive to cope with labor exploitation by raising wage rate.